iOS安全-混淆 Pass 分析 - Flattening
推荐 原创【iOS安全-混淆 Pass 分析 - Flattening】此文章归类为:iOS安全。
概述
代码扁平化的目的是将原有的程序逻辑重新组合成复杂逻辑,其主要体现是把原来的 if else语句转换成 switch语句。switch结构体包含多个分支,各个分支的执行顺序是随机的,但并不影响真正的程序逻辑。然后在 switch结构的外层,再套一个或多个 while循环。
下面编写一段代码进行测试,代码的功能是在 main函数中执行一个名称为 add的自定义函数。add函数里会判断参数 num1 是否等于 100,如果等于,则返回 0,否则继续执行,而后将参数 num1和 num2相加,结果赋值给 num3,并返回 num3。具体代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | int add(int num1, int num2){ if (num1 == 100) { return 0; } int num3 = num1 + num2; return num3;}int main(){ int num1 = 10; int num2 = 20; int num3 = add(num1,num2); return 0;} |
编译上面的代码,使用 IDA 反编译可执行文件,会看到代码的调用过程非常简单,很容易被分析,如图所示:
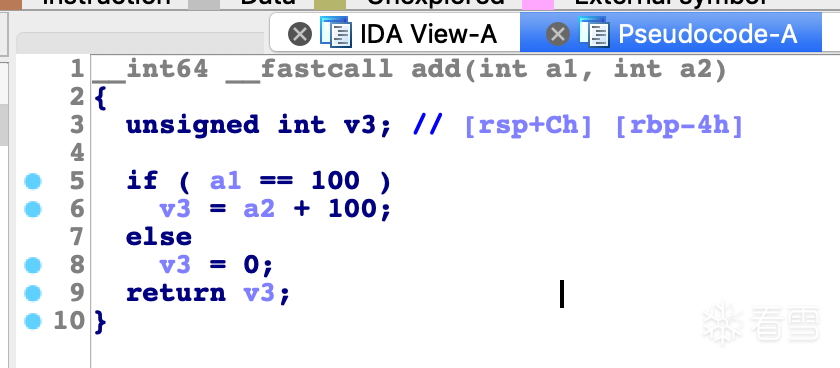
源码分析
obfuscator-llvm 中有一个代码扁平化的 Pass,名称为 flattening,接下来我们抽丝剥茧,一步步分析 flattening是怎么做到代码扁平化的。
首先使用 opt 进行调试。打开 Flattening.cpp,从第 39 行可以看到注册的 Pass 名称是 flattening;第 45 行调用 toObfuscate判断需要处理的函数是否有 fla标识(为了调试方便,我们将这部分代码注释掉),如果判断有,就调用flatten函数,这个函数是我们分析的关键。Flattening.cpp 文件的内容如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 | namespace {struct Flattening : public FunctionPass { static char ID; // Pass identification, replacement for typeid bool flag; Flattening() : FunctionPass(ID) {} Flattening(bool flag) : FunctionPass(ID) { this->flag = flag; } bool runOnFunction(Function &F); bool flatten(Function *f);};}char Flattening::ID = 0;static RegisterPass<Flattening> X("flattening", "Call graph flattening");Pass *llvm::createFlattening(bool flag) { return new Flattening(flag); }bool Flattening::runOnFunction(Function &F) { Function *tmp = &F; // Do we obfuscate if (toObfuscate(flag, tmp, "fla")) { if (flatten(tmp)) { ++Flattened; } } return false;} |
在 flatten函数的入口设置断点,在 lldb 后面输入命令 po f->dump(),打印参数 F,输出 add函数的所有中间层代码,代码如下,为了方便理解,每一行都做了相应注释:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 | ; Function Attrs: noinline nounwind ssp uwtabledefine i32 @add(i32 %num1, i32 %num2) #0 {entry: ;第 1 个 BasicBlock,名称是 entry %retval = alloca i32, align 4 ;为返回值分配 4 字节空间 %num1.addr = alloca i32, align 4 ;为变量 num1.addr 分配 4 字节空间 %num2.addr = alloca i32, align 4 ;为变量 num2.addr 分配 4 字节空间 %num3 = alloca i32, align 4 ;为变量 num3 分配 4 字节的空间 store i32 %num1, i32* %num1.addr, align 4 ;将变量 num1 保存到 num1.addr store i32 %num2, i32* %num2.addr, align 4 ;将变量 num2 保存到 num2.addr %0 = load i32, i32* %num1.addr, align 4 ;将变量 num1.addr 保存到变量 0 %cmp = icmp ne i32 %0, 100 ;比较变量 0 是否等于 100 br i1 %cmp, label %if.then, label %if.end ;如果条件比较成立则会跳转到 if.then if.then: ;第 2 个 BasicBlock,名称是 if.then ; preds = %entry store i32 0, i32* %retval, align 4 br label %return ;跳转到 return if.end: ;第 3 个 BasicBlock,名称是 if.end ; preds = %entry %1 = load i32, i32* %num1.addr, align 4 ;将变量 num1.addr 保存到变量 1 %2 = load i32, i32* %num2.addr, align 4 ;将变量 num2.addr 保存到变量 2 %add = add nsw i32 %1, %2 ;将变量 1 和变量 2 相加,结果保存到变量 add store i32 %add, i32* %num3, align 4 ;将变量 add 保存到变量 num3 %3 = load i32, i32* %num3, align 4 ;将变量 num3 保存到变量 3 store i32 %3, i32* %retval, align 4 ;将变量 3 保存到变量 retval br label %return ;跳转到 return return: ;第 4 个 BasicBlock,名称是 return ; preds = %if.end, %if.then %4 = load i32, i32* %retval, align 4 ret i32 %4} |
可以看出,一共有 4 个 BasicBlock,分别是 entry、if.then、if.end和 return。第 63 行是 flatten
函数要执行的第一条代码,第 63 行和第 64 行的作用是生成随机数(下方代码),这个在后面会用到:
1 2 3 | 62 //生成随机数63 char scrambling_key[16];64 llvm::cryptoutils->get_bytes(scrambling_key, 16); |
第 68 行和第 69 行的作用是将代码中的 switch语句转换成 if语句:
1 2 3 | 67 //转换 switch 语句68 FunctionPass *lower = createLowerSwitchPass();69 lower->runOnFunction(*f); |
紧接着,第 72 行到第 80 行的作用是保存原始的 BasicBlock到 origBB 容器:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | 71 //保存所有原始的 BasicBlock72 for (Function::iterator i = f->begin(); i != f->end(); ++i) {73 BasicBlock *tmp = &*i;74 origBB.push_back(tmp);7576 BasicBlock *bb = &*i;77 if (isa<InvokeInst>(bb->getTerminator())) {78 return false;79 }80 } |
第 88 行的作用是清空 origBB 容器里的第一个BasicBlock,因为第一个BasicBlock需要单独处理:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | 87 //清空第一个 BasicBlock88 origBB.erase(origBB.begin());8990 //获取指向第一个 BasicBlock 的指针91 Function::iteratortmp = f->begin(); //++tmp;92 BasicBlock *insert = &*tmp;93 |
第 95 行到第 98 行的作用是判断第一个BasicBlock是否含有条件语句,如果有,就获取条件语句的内容,并赋给br变量:
1 2 3 4 5 | 94 //如果第一个 BasicBlock 含有条件语句95 BranchInst *br = NULL;96 if (isa<BranchInst>(insert->getTerminator())) {97 br = cast<BranchInst>(insert->getTerminator());98 } |
获取的内容如下:
1 | br i1 %cmp, label %if.then, label %if.end |
第 100 行到第 107 行的作用是获取第一个BasicBlock的倒数第二行:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | 100 if ((br != NULL && br->isConditional()) ||101 insert->getTerminator()->getNumSuccessors() > 1) {102 BasicBlock::iterator i = insert->end();103 --i;104105 if (insert->size() > 1) {106 --i;107 }108 |
获取的内容如下:
1 | %cmp = icmp ne i32 %0, 100 |
第 109 行的作用是对 BasicBlock进行分割,第 110 行是将分割后的内容放入 origBB 容器的第一条记录中,还记得第88 行清空了origBB容器的第一条记录吧?
1 2 3 4 | 109 BasicBlock *tmpBB = insert->splitBasicBlock(i, "first");110 origBB.insert(origBB.begin(), tmpBB);111 }112 |
分割后 tmp得到的内容如下:
1 2 3 | first: ; preds = %entry %cmp = icmp ne i32 %0, 100 br i1 %cmp, label %if.then, label %if.end |
分割后 insert 的内容如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | entry: %retval = alloca i32, align 4 %num1.addr = alloca i32, align 4 %num2.addr = alloca i32, align 4 %num3 = alloca i32, align 4 store i32 %num1, i32* %num1.addr, align 4 store i32 %num2, i32* %num2.addr, align 4 %0 = load i32, i32* %num1.addr, align 4 br label %first |
第 114 行是移除跳转语句,也就是将 br label%first移除:
1 2 | 113 // 移除跳转114 insert->getTerminator()->eraseFromParent(); |
第 117 行到第 122 行的作用是创建 switch语句需用的变量 switchVar,变量的值就是最前面第 63 行和第 64 行随机生成的 scrambling_key:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | 116 //创建 switchVar,并按其进行设置117 switchVar = new AllocaInst(Type::getInt32Ty(f->getContext()), 0, "switchVar", insert);118119 new StoreInst(120 ConstantInt::get(Type::getInt32Ty(f->getContext()),121 llvm::cryptoutils->scramble32(0, scrambling_key)),122 switchVar, insert); |
创建好 switchVar之后,再打印 insert,可以看到其内容的最后多了两条语句:
1 2 | %switchVar = alloca i32store i32 1207049111, i32* %switchVar |
第 125 行的作用是创建 loopEntry和 loopEnd,此时里面的代码还是空的。第 128 行是创建一条 load指令,将 switchvar放入 loopEntry中。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 | 124 //创建主循环125 loopEntry = BasicBlock::Create(f->getContext(), "loopEntry", f, insert);126 loopEnd = BasicBlock::Create(f->getContext(), "loopEnd", f, insert);127128 load = new LoadInst(switchVar, "switchVar", loopEntry);129130 //在顶部移动第一个 BasicBlock131 insert->moveBefore(loopEntry);132 BranchInst::Create(loopEntry, insert);133134 //从 loopEnd 跳转到 loopEntry135 BranchInst::Create(loopEntry, loopEnd);136137 BasicBlock *swDefault = BasicBlock::Create(f->getContext(), "switchDefault", f, loopEnd);138139 BranchInst::Create(loopEnd, swDefault);140141 //创建 switch 语句本身,并设置条件142 switchI = SwitchInst::Create(&*f->begin(), swDefault, 0, loopEntry);143 switchI->setCondition(load);144145 //移除第一个BasicBlock 中的跳转分支,并且创建一个到 while 循环的跳转146 f->begin()->getTerminator()->eraseFromParent();147148 BranchInst::Create(loopEntry, &*f->begin()); //添加上 br label %loopEntry |
第 151 行到第 164 行的作用是给 origBB 里每个的 BasicBlock 填充 switch分支:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | 150 //把所有 BasicBlock 都放入 switch 分支151 for (vector<BasicBlock *>::iterator b = origBB.begin(); b != origBB.end();152 ++b) {153 BasicBlock *i = *b;154 ConstantInt *numCase = NULL;155156 //把 BasicBlock 移动到 switch 内(只是视觉上的,不涉及代码逻辑)157 i->moveBefore(loopEnd);158159 //给 switch 添加 case,switchVar 是随机数160 numCase = cast<ConstantInt>(ConstantInt::get(161 switchI->getCondition()->getType(),162 llvm::cryptoutils->scramble32(switchI->getNumCases(), scrambling_key)));163 switchI->addCase(numCase, i); //添加 switch case164 } |
经过上面一番处理之后,得到的代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 | (lldb) po f->dump(); Function Attrs: noinline nounwind ssp uwtabledefine i32 @add(i32 %num1, i32 %num2) #0 { entry: %retval = alloca i32, align 4 %num1.addr = alloca i32, align 4 %num2.addr = alloca i32, align 4 %num3 = alloca i32, align 4 store i32 %num1, i32* %num1.addr, align 4 store i32 %num2, i32* %num2.addr, align 4 %0 = load i32, i32* %num1.addr, align 4 %switchVar = alloca i32 store i32 1207049111, i32* %switchVar br label %loopEntry loopEntry: ; preds = %entry,%loopEnd %switchVar1 = load i32, i32* %switchVar switch i32 %switchVar1, label %switchDefault [ i32 1207049111, label %first i32 -677357051, label %if.then i32 -1251090459, label %if.end i32 1194405227, label %return ] switchDefault: ; preds = %loopEntry br label %loopEnd first: ; preds = %loopEntry %cmp = icmp ne i32 %0, 100 br i1 %cmp, label %if.then, label %if.end if.then: ; preds = %loopEntry,%first store i32 0, i32* %retval, align 4 br label %return if.end: ; preds = %loopEntry, %first %1 = load i32, i32* %num1.addr, align 4 %2 = load i32, i32* %num2.addr, align 4 %add = add nsw i32 %1, %2 store i32 %add,i32* %num3, align 4 %3 = load i32, i32* %num3, align 4 store i32 %3, i32* %retval, align 4 br label %return return: ; preds = %loopEntry, %if.end, %if.then %4 = load i32, i32* %retval, align 4 ret i32 %4 loopEnd: ; preds = %switchDefault br label %loopEntry} |
可以看出,扁平化效果已经实现了,loopEntry和 loopEnd是一个 while循环,while循环中有一个 switch结构,switch结构中有 4 个 case分支,分别是 first、if.then、if.end、return。如果 switchVar的值是1207049111,就跳转到 first分支;如果是-677357051,则跳转到 if.then;如果是 -125090459,跳转到 if.end分支;如果是1194405227,跳转到 return分支。
可以看到,上面得到的中间层代码中已经有 switch结构了,但是在执行跳转时并没有更新 switchVar,这样会使真实的程序逻辑没有正确执行。第 166 行到第 237 行的作用就是更新 switchVar,因为只有一个后续块相当于无条件跳转,所以直接将switchVar更新成后续块对应的 case:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 | 166 //重新计算 switchVar167 for (vector<BasicBlock *>::iterator b = origBB.begin(); b != origBB.end();168 ++b) {169 BasicBlock *i = *b;170 ConstantInt *numCase = NULL;171172 // Ret BasicBlock 是个返回块,不需要更新 caseVar173 if (i->getTerminator()->getNumSuccessors() == 0) {174 continue;175 }176177 //如果是无条件跳转178 if (i->getTerminator()->getNumSuccessors() == 1) {179 // Get successor and delete terminator180 BasicBlock *succ = i->getTerminator()->getSuccessor(0);181 i->getTerminator()->eraseFromParent();182183 //获取下一个 case 分支184 numCase = switchI->findCaseDest(succ);185186 // If next case == default case (switchDefault)187 if (numCase == NULL) {188 numCase = cast<ConstantInt>(189 ConstantInt::get(switchI->getCondition()->getType(),190 llvm::cryptoutils->scramble32(191 switchI->getNumCases() - 1, scrambling_key)));192 }193194 //更新 switchVar,并且跳转到循环尾部195 new StoreInst(numCase, load->getPointerOperand(), i); //store 给%switchVar 赋值为 numCase196 BranchInst::Create(loopEnd, i); //插入 br label %loopEnd197 continue;198 }199200 //If it's a conditional jump //有两个后续块,也就是条件跳转,successor 对象就是后续块的意思201 if (i->getTerminator()->getNumSuccessors() == 2) {202 //获取接下来的 case 分支203 ConstantInt *numCaseTrue =204 switchI->findCaseDest(i->getTerminator()->getSuccessor(0));205 ConstantInt *numCaseFalse =206 switchI->findCaseDest(i->getTerminator()->getSuccessor(1));207208 //检查 next case 和 default case (switchDefault) 是否相等209 if (numCaseTrue == NULL) {210 numCaseTrue = cast<ConstantInt>(numCaseTrue = cast<ConstantInt>(211 ConstantInt::get(switchI->getCondition()->getType(),212 llvm::cryptoutils->scramble32(213 switchI->getNumCases() - 1, scrambling_key)));214 }215216 if (numCaseFalse == NULL) {217 numCaseFalse = cast<ConstantInt>(218 ConstantInt::get(switchI->getCondition()->getType(),219 llvm::cryptoutils->scramble32(220 switchI->getNumCases() - 1, scrambling_key)));221 }222223 // Create a SelectInst %1 = select i1 %cmp, i32 117441206, i32 -880348549224 BranchInst *br = cast<BranchInst>(i->getTerminator());225 SelectInst *sel =226 SelectInst::Create(br->getCondition(), numCaseTrue, numCaseFalse, "",227 i->getTerminator());228229 //清除终止符230 i->getTerminator()->eraseFromParent();231232 //更新 switchVar,并且跳转到循环尾部233 new StoreInst(sel, load->getPointerOperand(), i);234 BranchInst::Create(loopEnd, i);235 continue;236 }237 }238239 fixStack(f); |
最后我们看看最终的中间层代码是什么样的,完整的代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 | (lldb) po f->dump(); Function Attrs: noinline nounwind ssp uwtabledefine i32 @add(i32 %num1, i32 %num2) #0 {entry: %.reg2mem = alloca i32 %retval = alloca i32, align 4 %num1.addr = alloca i32, align 4 %num2.addr = alloca i32, align 4 %num3 = alloca i32, align 4 store i32 %num1, i32* %num1.addr, align 4 store i32 %num2,i32* %num2.addr, align 4 %0 = load i32, i32* %num1.addr, align 4 store i32 %0, i32* %.reg2mem %switchVar = alloca i32 store i32 1207049111, i32* %switchVar br label %loopEntry loopEntry: ; preds = %entry, %loopEnd %switchVar1 = load i32, i32* %switchVar switch i32 %switchVar1, label %switchDefault [ i32 1207049111, label %first i32 -677357051, label %if.then i32 -1251090459, label %if.end i32 1194405227, label %return ] switchDefault: ; preds = %loopEntry br label %loopEnd first: ; preds = %loopEntry %.reload = load volatile i32, i32* %.reg2mem %cmp = icmp ne i32 %.reload, 100 %1 = select i1 %cmp, i32 -677357051, i32 -1251090459 store i32 %1, i32* %switchVar br label %loopEnd if.then: ; preds = %loopEntry store i32 0, i32* %retval, align 4 store i32 1194405227, i32* %switchVar br label %loopEnd if.end: ; preds = %loopEntry %2 = load i32, i32* %num1.addr, align 4 %3 = load i32, i32* %num2.addr, align 4 %add = add nsw i32 %2, %3 store i32 %add, i32* %num3, align 4 %4 = load i32, i32* %num3, align 4 store i32 %4, i32* %retval, align 4 store i32 1194405227, i32* %switchVar br label %loopEnd return: ; preds = %loopEntry %5 = load i32, i32* %retval, align 4 ret i32 %5 loopEnd: ; preds = %if.end,%if.then, %first, %switchDefault br label %loopEntry } |
可以看到,first、if.then、if.end这三个 BasicBlock的代码都会更新 switchVar,这样便达到了混淆代码逻辑的效果,并且不影响真实的程序逻辑。至此,整个代码扁平化的过程全部分析完。
总结
该文章只是针对最初版本的 OLLVM 中的 Flatttening Pass 进行了分析,通过简单的例子简述平坦化的实现步骤。但由于该仓库对应的 LLVM 版本较低,读者可以阅读最近的适配版本进行理解,整体思路相同,很多细节处理可能存在差异,比如OLLVM-17 在代码结构、可读性、上下文管理、随机数生成、代码简洁性和调试标识等方面表现更好,或者Hikari中使用了 DataLayout 来获取数据布局信息,同时增加了对异常处理的检查和调试信息的输出,读者感兴趣也可以调试看下具体实现细节。
更多【iOS安全-混淆 Pass 分析 - Flattening】相关视频教程:www.yxfzedu.com
相关文章推荐
- Android安全-frida源码编译详解 - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 软件逆向- PE格式:新建节并插入代码 - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 加壳脱壳- UPX源码学习和简单修改 - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 二进制漏洞-win越界写漏洞分析 CVE-2020-1054 - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- Pwn-2022长城杯决赛pwn - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 软件逆向-Wibu Codemeter 7.3学习笔记——Codemeter服务端 - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- Pwn-沙箱逃逸之google ctf 2019 Monochromatic writeup - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 软件逆向-Wibu Codemeter 7.3学习笔记——AxProtector壳初探 - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 企业安全-学习Kubernetes笔记——暴露站点服务(Ingress) - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 企业安全-学习Kubernetes笔记——部署数据库站点(MySql) - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 企业安全-学习Kubernetes笔记——部署web站点环境(PHP+Nginx) - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 企业安全-学习Kubernetes笔记——安装NFS驱动 - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 企业安全-学习Kubernetes笔记——kubeadm安装Kubernetes - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 软件逆向-wibu软授权(四) - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 软件逆向-使用IDAPython开发复制RVA的插件 - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 2-wibu软授权(三) - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 软件逆向-wibu软授权(二) - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 软件逆向-wibu软授权(一) - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 软件逆向- PE格式:分析IatHook并实现 - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- Android安全-安卓API自动化安全扫描 - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
2):严禁色情、血腥、暴力
3):严禁发布任何形式的广告贴
4):严禁发表关于中国的政治类话题
5):严格遵守中国互联网法律法规
6):有侵权,疑问可发邮件至service@yxfzedu.com
- (未完,保存下)Windows NTFS本地提权漏洞 CVE-2021-31956
- 逆向Pyinstaller打包的程序源码及保护
- CTF 《2015移动安全挑战赛》第二题 AliCrackme_2 逆向
- 腾讯WeTest "6.18品质服务狂欢节":狂欢优惠,燃动六月!
- CTF 《2015移动安全挑战赛》第一题 AliCrackme_1 逆向
- 超过10万个 ChatGPT 用户数据被盗出售,AIGC时代如何安全地使用ChatGPT?
- C++利用活跃变量分析清除基本块中的垃圾指令
- 代码管理器 CodeManager v1.2.4
- 攻击面管理是威胁驱动到风险驱动演进的最佳实践
- SecOps2023|李少鹏独家解读《原子化安全能力白皮书》