首页/文章/CTF对抗/软件逆向- IDAPython 系列 —— 画出两个函数的交叉引用图/
软件逆向- IDAPython 系列 —— 画出两个函数的交叉引用图
推荐 原创第一次在论坛平台投稿,还是有点忐忑的,一直想分享些 idapython 的内容,网上现在的内容太少,都只是教了一些基础的用法。官方的文档和例子又比较散。希望我的分享能让大家更加快乐的逆向吧,哈哈!
这是这个系列的第一篇,分享一下如何用IDAPython 画出两个函数之间的交叉引用图,可视化一直是我很喜欢的一个东西,逆向的目的就是理解代码嘛,可视化是理解代码的一个很重要的工具。
开发环境:
- Python3.8
- IDA Pro 7.7+
此外,本教程的实现还依赖了几个 Python 包:
- sark
- networkx
- matplotlib
本教程安排如下:
- 定义递归函数 find_cross_refs
- IDAPython Action 概念介绍
- 添加我们的 Action
- 最终效果
一、定义递归函数 find_cross_refs
在这里,我们定义了一个名为 find_cross_refs 的递归函数,用于查找两个函数之间的交叉引用关系。该函数包含以下参数:
- func: sark.Function 类型,表示要查找交叉引用关系的起始函数对象。
- target_func: sark.Function 类型,表示要查找交叉引用关系的目标函数对象。
- G: networkx.DiGraph 类型,表示用于存储函数之间引用关系的有向图对象。
- max_depth: int 类型,表示查找引用关系的最大深度。
- include_data_xref: bool 类型,表示在查找引用关系时是否要包含数据引用关系。
函数中主要分为以下几个步骤:
- 首先判断查找引用关系的深度是否达到最大深度,如果达到最大深度就直接返回 False。
- 然后根据 include_data_xref 的设置,获取该函数中所有的引用 refes。如果 include_data_xref 为 True,则获取所有数据引用关系,否则获取所有函数调用引用关系。
- 遍历函数的所有引用 ref,如果该引用 ref 指向目标函数,则在有向图 G 中通过 add_edge 函数添加一条从当前函数到目标函数的边,并返回 True。
- 如果引用指向另一个函数,则递归调用 find_cross_refs 函数查找两个函数之间的交叉引用关系。
- 如果所有引用遍历完,仍然没有找到交叉引用,则返回 False。
下面是 find_cross_refs 函数的详细实现代码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
|
MAX_SEARCH_DEPTH
=
10
# 定义递归函数,用于查找两个函数之间的交叉引用关系
def
find_cross_refs(func: sark.Function, target_func, G, max_depth, include_data_xref):
if
max_depth
=
=
0
:
return
False
max_depth
-
=
1
# 获取函数的所有引用
if
include_data_xref:
refs
=
list
(func.xrefs_from)
else
:
refs
=
list
(func.calls_from)
# 遍历函数的每一个引用
for
ref
in
refs:
# 获取引用的地址
ref_addr
=
ref.to
# type: ignore
# 判断引用是否指向目标函数
if
ref_addr
=
=
target_func.start_ea:
# 如果指向目标函数,则找到了交叉引用关系
# 在图中添加一条边表示函数之间的引用关系
# G.add_node(func, name=func.demangled)
# G.add_node(target_func, name=target_func.demangled)
G.add_edge(func.ea, target_func.ea)
return
True
# 如果引用指向另一个函数,则递归调用find_cross_refs函数,查找两个函数之间的交叉引用关系
seg
=
sark.Segment(ea
=
ref_addr)
if
seg.name !
=
"__text"
:
#是 external Function
continue
else
:
try
:
ref_func
=
sark.Function(ea
=
ref_addr)
except
Exception as e:
print
(e)
continue
if
find_cross_refs(ref_func, target_func, G, max_depth, include_data_xref):
# 如果找到了交叉引用关系,则在图中添加一条边表示函数之间的引用关系
# G.add_node(func, name=func.demangled)
# G.add_node(ref_func, name=ref_func.demangled)
G.add_edge(func.ea, ref_func.ea)
return
True
# 如果遍历完所有引用后仍然没有找到交叉引用关系,则返回False
return
False
|
二、IDApython Action 概念介绍
- action 首先需要被注册。一旦被注册,action 可以用快捷键触发(如果指定了的话),但是 action 还没法在 UI 中看到
- action 被注册之后,我们可以将 action attach 到以下三个地方
- 主菜单
- Toolbar
- 上下文菜单
- 同一个 action 可以在不同的地方被使用
- 一个 action 有一个 handler,是一个结构体带有以下两个 callback
- activate callback,当 action 触发时调用
- update callback,声明 action 是否 enabled
给一段代码,看一下如何注册一个 Action
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
# 1) Create the handler class
class
MyHandler(idaapi.action_handler_t):
def
__init__(
self
):
idaapi.action_handler_t.__init__(
self
)
# Say hello when invoked.
def
activate(
self
, ctx):
print
"Hello!"
return
1
# This action is always available.
def
update(
self
, ctx):
return
idaapi.AST_ENABLE_ALWAYS
# 2) Describe the action
action_desc
=
idaapi.action_desc_t(
'my:action'
,
# The action name. This acts like an ID and must be unique
'Say hello!'
,
# The action text.
MyHandler(),
# The action handler.
'Ctrl+H'
,
# Optional: the action shortcut
'Says hello'
,
# Optional: the action tooltip (available in menus/toolbar)
199
)
# Optional: the action icon (shows when in menus/toolbars)
# 3) Register the action
idaapi.register_action(action_desc)
|
然后是将 action 放到 UI 上的代码
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
# 将 action 放到菜单中
idaapi.attach_action_to_menu(
'Edit/Other/Manual instruction...'
,
# The relative path of where to add the action
'my:action'
,
# The action ID (see above)
idaapi.SETMENU_APP)
# We want to append the action after the 'Manual instruction...'
# 将 action 放到 toolbar 中
idaapi.attach_action_to_toolbar(
"AnalysisToolBar"
,
# The toolbar name
'my:action'
)
# The action ID
# 将 action 永久的放到某个 widget 的上下文菜单中
# Create a widget, or retrieve a pointer to it.
form
=
idaapi.get_current_tform()
idaapi.attach_action_to_popup(form,
None
,
"my:action"
,
None
)
|
了解完这些我们就可以写自己的 Action 了,为了方便我对官方的 Action api 做了一些封装, 下面是我自己的 action.py 文件
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
|
import
idaapi
from
.hookers
import
global_hooker_manager
from
typing
import
Optional
class
ActionManager(
object
):
def
__init__(
self
):
self
.__actions
=
[]
def
register(
self
, action):
self
.__actions.append(action)
idaapi.register_action(
idaapi.action_desc_t(action.name, action.description, action, action.hotkey)
)
if
isinstance
(action, HexRaysPopupAction):
global_hooker_manager.register(HexRaysPopupRequestHandler(action))
def
initialize(
self
):
pass
def
finalize(
self
):
for
action
in
self
.__actions:
idaapi.unregister_action(action.name)
action_manager
=
ActionManager()
class
Action(idaapi.action_handler_t):
"""
Convenience wrapper with name property allowing to be registered in IDA using ActionManager
"""
description: Optional[
str
]
=
None
hotkey: Optional[
str
]
=
None
def
__init__(
self
):
super
(Action,
self
).__init__()
@property
def
name(
self
):
return
"HexRaysPyTools:"
+
type
(
self
).__name__
def
activate(
self
, ctx: idaapi.action_ctx_base_t):
raise
NotImplementedError
def
update(
self
, ctx: idaapi.action_ctx_base_t):
# return idaapi.AST_XXX
# 通常会根据 ctx.widget_type == idaapi.BWN_XXX 来判断当前是在哪个窗口
raise
NotImplementedError
class
HexRaysPopupAction(Action):
"""
Wrapper around Action. Represents Action which can be added to menu after right-clicking in Decompile window.
Has `check` method that should tell whether Action should be added to popup menu when different items
are right-clicked.
Children of this class can also be fired by hot-key without right-clicking if one provided in `hotkey`
static member.
"""
def
__init__(
self
):
super
(HexRaysPopupAction,
self
).__init__()
def
activate(
self
, ctx: idaapi.action_ctx_base_t):
raise
NotImplementedError
def
check(
self
, hx_view):
# type: (idaapi.vdui_t) -> bool
raise
NotImplementedError
def
update(
self
, ctx: idaapi.action_ctx_base_t):
if
ctx.widget_type
=
=
idaapi.BWN_PSEUDOCODE:
return
idaapi.AST_ENABLE_FOR_WIDGET
return
idaapi.AST_DISABLE_FOR_WIDGET
class
HexRaysPopupRequestHandler(idaapi.Hexrays_Hooks):
def
__init__(
self
, action):
super
().__init__()
self
.__action
=
action
def
populating_popup(
self
, widget, popup_handle, vu):
if
self
.__action.check(vu):
idaapi.attach_action_to_popup(widget, popup_handle,
self
.__action.name,
None
)
return
0
|
三、添加我们的 Action
然后我们开始定义显示交叉引用图的 Action,我把它叫做 XrefRoadMapAction
具体来说,该类包含以下方法:
- check 方法:返回 True 表示该操作可用。
- activate 方法:执行实际的操作,该方法获取当前函数地址,获取用户输入的目标函数地址,并创建一个有向图进行处理。
- update 方法:更新当前操作的 UI(例如菜单项)的图形状态。
可以看出,该类实现的核心是 activate 方法。其主要流程如下:
- 获取当前光标所在的函数对象;
- 获取用户输入的目标函数地址;
- 创建空的有向图对象 G;
- 根据用户设置调用 find_cross_refs 函数搜索从当前函数到目标函数的交叉引用路径;
- 如果在搜索结果中找到了交叉引用路径,则在 G 中添加表示函数之间引用关系的边,然后使用 sark.ui.NXGraph 绘制有向图;
- 如果没有找到路径,则显示一个警告信息。
下面是 XrefRoadMapAction 类的详细实现代码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
|
class
XrefRoadMapAction(HexRaysPopupAction):
"""
Convenience wrapper with name property allowing to be registered in IDA using ActionManager
"""
description: Optional[
str
]
=
"Find Xref Road map between A and B"
hotkey: Optional[
str
]
=
"Alt-F3"
def
__init__(
self
):
super
(Action,
self
).__init__()
def
check(
self
, hx_view: idaapi.vdui_t)
-
>
bool
:
return
True
def
activate(
self
, ctx: idaapi.action_ctx_base_t):
# 获取光标所在的函数地址
cur_ea
=
idaapi.get_screen_ea()
try
:
cur_func
=
sark.Function(ea
=
cur_ea)
except
Exception as e:
traceback.print_exc()
# 如果光标不在函数中,则提示错误
print
(
"Error: cursor is not in a function!"
)
return
# 获取用户输入的目标函数的地址
target_func_addr
=
idaapi.ask_addr(defval
=
0
,
format
=
"Enter target function address:"
)
if
target_func_addr
=
=
idaapi.BADADDR
or
target_func_addr
is
None
:
# 如果用户输入的是无效的地址,则提示错误
print
(
"Error: invalid target function address!"
)
return
# 获取目标函数的函数对象
try
:
s
=
sark.Segment(ea
=
target_func_addr)
if
s.name
=
=
"UNDEF"
:
target_func
=
sark.ExternFunction(ea
=
target_func_addr)
else
:
target_func
=
sark.Function(ea
=
target_func_addr)
# type: ignore
except
Exception as e:
# 如果目标函数不存在,则提示错误
traceback.print_exc()
print
(
"Error: target function does not exist!"
)
return
import
networkx as nx
# 创建有向图
G
=
nx.DiGraph()
# 在这里实现查找两个函数之间交叉引用关系的代码...
print
(f
"find a path between func {cur_func.demangled} and {target_func.demangled}, max search depth is {MAX_SEARCH_DEPTH}"
)
btn_selected
=
idaapi.ask_yn(idaapi.ASKBTN_NO,
"是否包括 data xrefs?"
)
if
btn_selected
=
=
idaapi.ASKBTN_CANCEL:
return
ret
=
find_cross_refs(cur_func, target_func, G, MAX_SEARCH_DEPTH, include_data_xref
=
True
if
btn_selected
=
=
idaapi.ASKBTN_YES
else
False
)
if
ret
=
=
False
:
assert
len
(G.nodes())
=
=
0
,
"find_cross_refs 返回 False,但是 G 中有节点"
if
len
(G.nodes()) >
0
:
# 绘制图
G.nodes[cur_func.ea][sark.ui.NXGraph.BG_COLOR]
=
0x80
title
=
f
"Path from `{cur_func.demangled}` to `{target_func.demangled}`"
# Create an NXGraph viewer
viewer
=
sark.ui.NXGraph(G, handler
=
sark.ui.AddressNodeHandler(), title
=
title)
# Show the graph
viewer.Show()
else
:
idaapi.warning(
"Cannot find a path!!!"
)
def
update(
self
, ctx: idaapi.action_ctx_base_t):
# 获取当前窗口的类型
widget_type
=
ctx.widget_type
# 如果当前窗口是反汇编或者反编译窗口,则菜单项可用
if
widget_type
=
=
idaapi.BWN_DISASM
or
widget_type
=
=
idaapi.BWN_PSEUDOCODE:
return
idaapi.AST_ENABLE_FOR_WIDGET
else
:
return
idaapi.AST_DISABLE_FOR_WIDGET
|
代码里面其实还用了很多 sark 库的函数,大家可以自己学习其用法,这个库是专门对 idapython 的 api 做封装的,比较 pythonic,非常好用,我自己也给这个库添加了很多新的功能。
四、最终效果
如下所示:
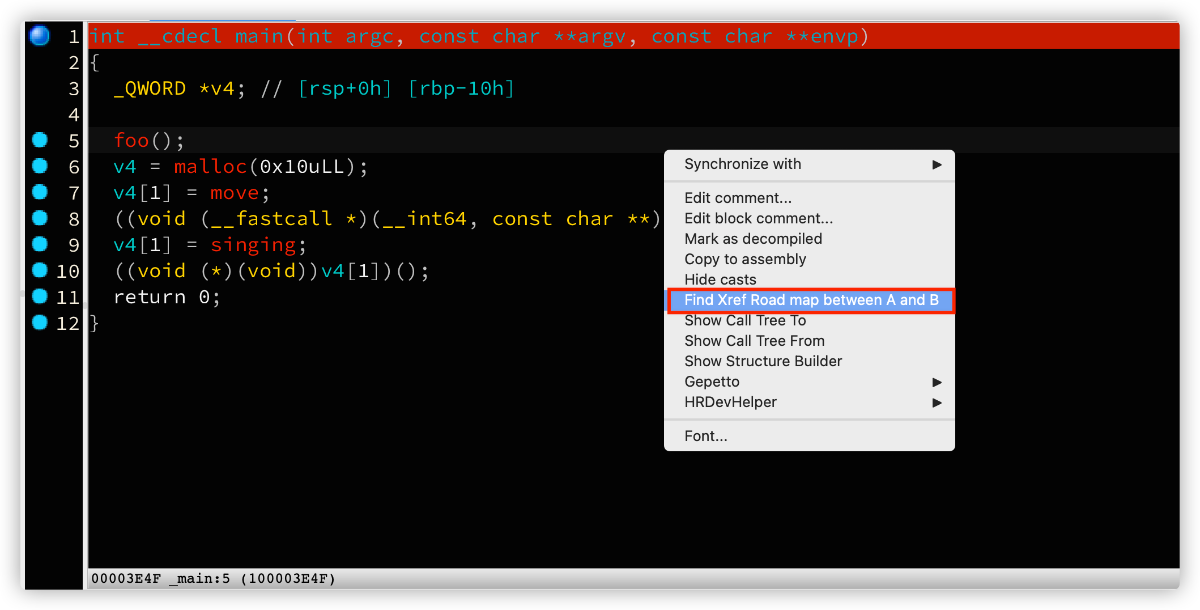
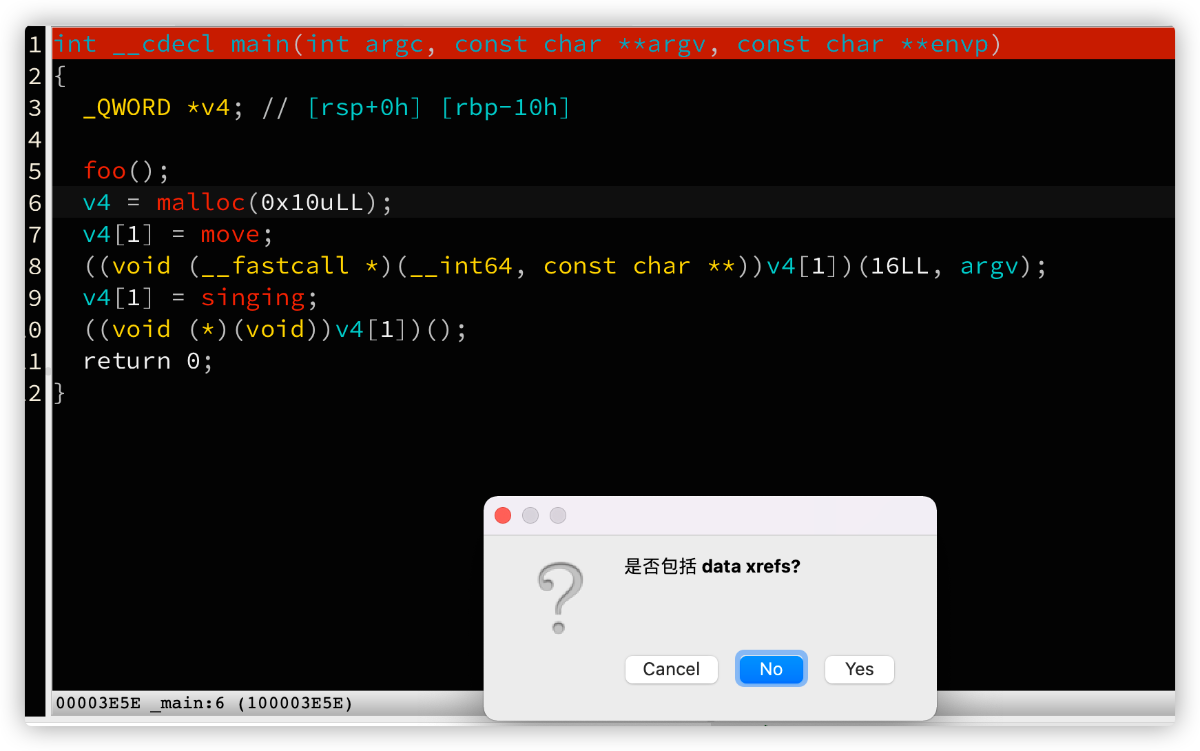
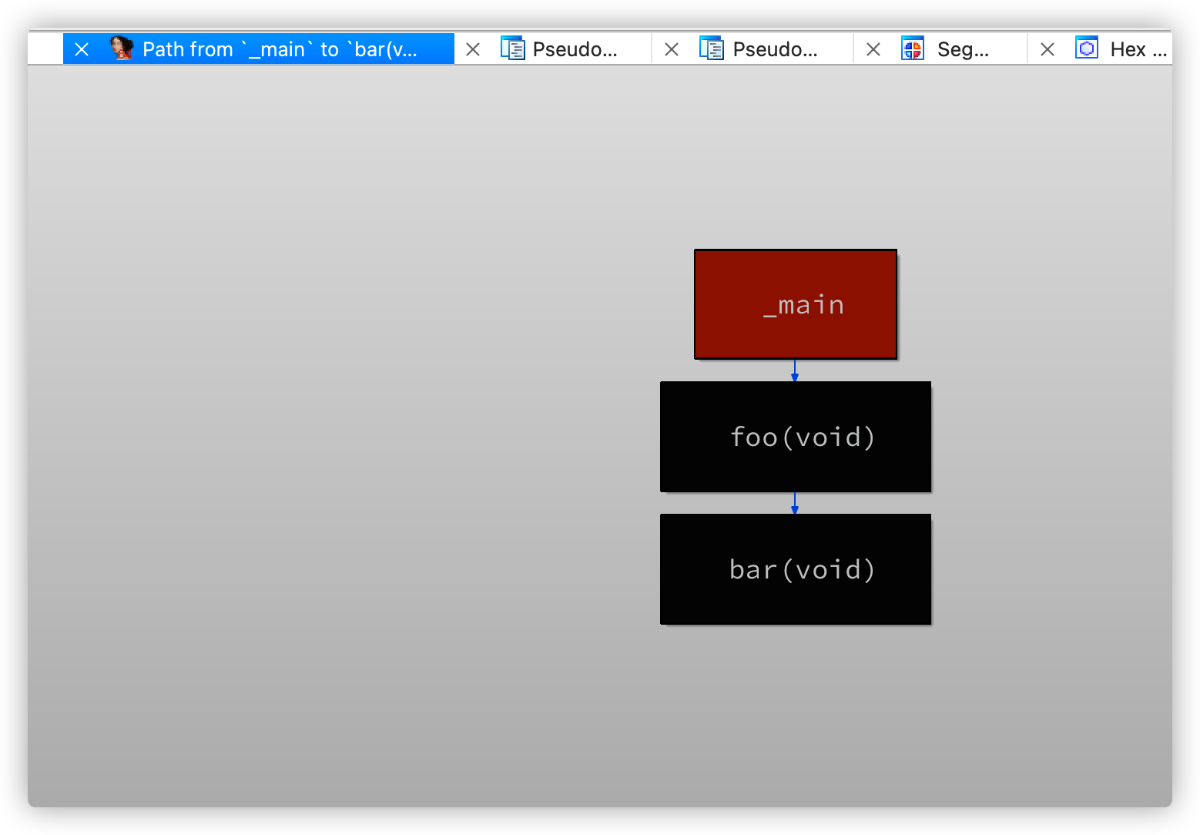
更多【 IDAPython 系列 —— 画出两个函数的交叉引用图】相关视频教程:www.yxfzedu.com
相关文章推荐
- 二进制漏洞-win越界写漏洞分析 CVE-2020-1054 - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- Pwn-2022长城杯决赛pwn - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 软件逆向-Wibu Codemeter 7.3学习笔记——Codemeter服务端 - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- Pwn-沙箱逃逸之google ctf 2019 Monochromatic writeup - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 软件逆向-Wibu Codemeter 7.3学习笔记——AxProtector壳初探 - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 企业安全-学习Kubernetes笔记——暴露站点服务(Ingress) - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 企业安全-学习Kubernetes笔记——部署数据库站点(MySql) - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 企业安全-学习Kubernetes笔记——部署web站点环境(PHP+Nginx) - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 企业安全-学习Kubernetes笔记——安装NFS驱动 - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 企业安全-学习Kubernetes笔记——kubeadm安装Kubernetes - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 软件逆向-wibu软授权(四) - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 软件逆向-使用IDAPython开发复制RVA的插件 - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 2-wibu软授权(三) - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 软件逆向-wibu软授权(二) - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 软件逆向-wibu软授权(一) - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 软件逆向- PE格式:分析IatHook并实现 - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- Android安全-安卓API自动化安全扫描 - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 二进制漏洞- Chrome v8 Issue 1307610漏洞及其利用分析 - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- iOS安全-IOS 脱壳入坑经验分享 - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 二进制漏洞-Windows UAF 漏洞分析CVE-2014-4113 - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
记录自己的技术轨迹
文章规则:
1):文章标题请尽量与文章内容相符
2):严禁色情、血腥、暴力
3):严禁发布任何形式的广告贴
4):严禁发表关于中国的政治类话题
5):严格遵守中国互联网法律法规
6):有侵权,疑问可发邮件至service@yxfzedu.com
近期原创 更多
- 编程技术- 驱动开发:通过Async反向与内核通信
- 加壳脱壳- [原创工具] FRIDA-JS-DEXDump 基于Frida的内存脱壳工具(学习frida-dexdump的成果)
- Pwn-小小做题家之——musl 1.2.2的利用手法
- 编程技术-cmake使用
- Pwn-手动编译测试musl1.2.2 meta dequeue特性
- 软件逆向-高级APT木马逆向分析
- Pwn-Pwn堆利用学习 —— FSOP、House of Orange —— ciscn_2019_n_7、House_of_Orange
- 软件逆向-国庆假期很闲之针对 VS2019 + WDK10 生成驱动关不掉pdb符号文件的研究
- 编程技术- 驱动通信:通过PIPE管道与内核层通信
- 软件逆向-基于PMI实现对读写行为检测