算法-《数据结构、算法与应用C++语言描述》-队列的应用-工厂仿真
推荐 原创工厂仿真
完整可编译运行代码见:Github::Data-Structures-Algorithms-and-Applications/_19Factory simulation/
问题描述
一个工厂有m台机器。工厂的每项任务都需要若干道工序才能完成。每台机器都执行一道工序,不同的机器执行不同的工序。一台机器一旦开始执行一道工序就不会中断,直到该工序完成为止。
举例
例 9-3 考察一个工厂,它有 3 台机器(m=3),有 4 项任务(n=4)。假设这 4 项任务都在0时刻出现,而且在仿真期间不再有新的任务。仿真过程一直持续到所有任务完成为止。
三台机器为 M1、M2 和 M3,它们的转换状态所花费的时间分别为2、3 和 1。因此,当一道工序完成时,机器M1必须等待2个时间单元才能启动下一道工序,机器M2必须等待3个时间单元才能启动下一道工序,机器M3必须等待1个时间单元才能启动下一道工序。
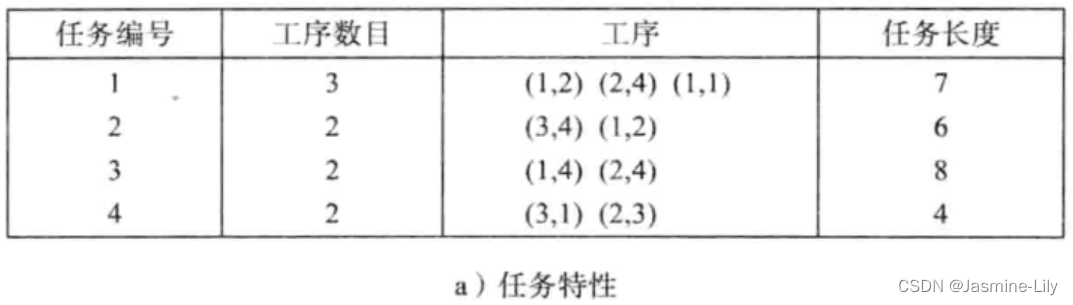
图9-16a分别列出了4项任务的特征。例如,1号任务有3道工序。每道工序用形如(机器,时间)的数对来描述。1号任务的第一道工序在M1上完成,需要2个时间单元;第二道工序在M2上完成,需要4个时间单元;第三道工序在 M1上完成,需要1个时间单元。各项任务的长度分别为7、6、8和4。
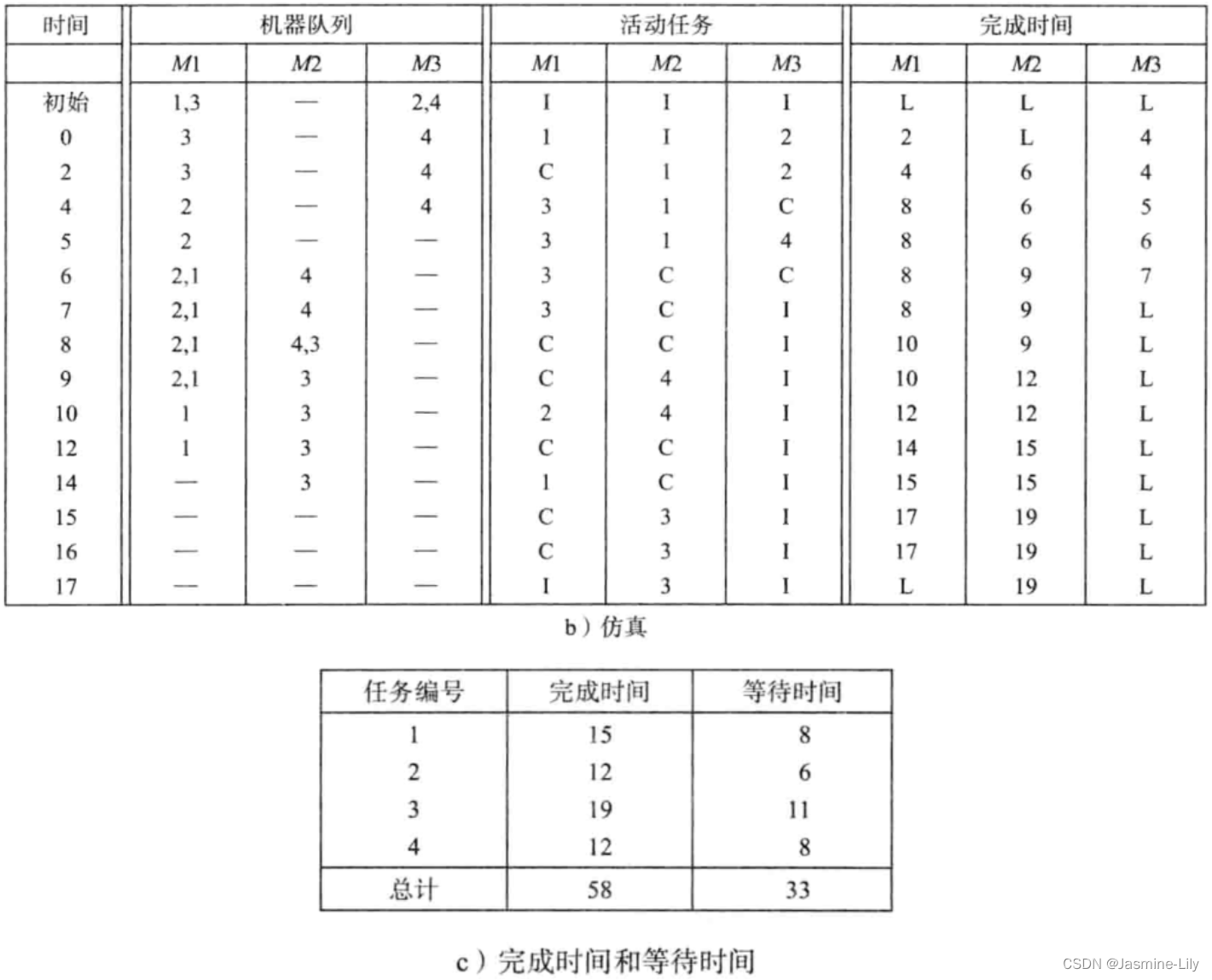
仿真从 0时刻开始。第一个事件即启动事件出现在 0时刻。此时,每个机器队列中的第一个任务被调度到相应的机器上执行。1号任务的第一道工序被调度到M1上执行,2号任务的第一道工序被调度到 M3 上执行。这时 M1 的队列中仅剩 3 号任务,而 M3 的队列中仅剩 4号任务,M2的队列仍然为空。这样,1号任务成为M1上的活动任务,2号任务成为M3上的活动任务,M2仍然为空闲。M1的结束时间变成2(当前时刻0+工序时间2),M3的结束时间变成 4。
下一个事件在时刻2出现,这个时刻是根据机器完成时间的最小值来确定的。在时刻2,M1 完成了它的当前活动工序。这个工序是 1 号任务的工序。1 号任务被移动到 M2 上以执行下一道工序。这时的 M2 是空闲的,因此立即执行 1 号任务的第二道工序,这道工序将在第 6时刻完成(当前时刻2+工序时间4)。M1进入转换工序(即转换状态)并持续2个时间单元。M1的活动任务被设置为C(转换状态),其完成时刻为4。
在时刻 4,M1 和 M3 完成了各自的当前工序。M1 完成的是“转换”工序,开始执行新的任务,从队列中选择第一个任务——3号任务。3 号任务第一个工序的长度为4,因此该工序的结束时间为8,M1的完成时间变为8。2号任务在M3上完成其第一道工序之后移至M1上继续执行,由于 M1正忙,所以 2号任务被放入 M1 的队列。M3进入转换状态,转换状态的结束时刻为 5。以此类推,能够推出剩余的事件序列。
代码
main.cpp
/*
Project name : allAlgorithmsTest
Last modified Date: 2022年8月13日17点38分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: main()函数,控制运行所有的测试函数
*/
#include "_22factorySim.h"
int main()
{
factorySimTest();
return 0;
}
_22factorySim.h
/*
Project name : allAlgorithmsTest
Last modified Date: 2022年8月17日09点22分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 工厂仿真头文件
*/
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include "_1myExceptions.h"
#include "_22task.h"
#include "_22job.h"
#include "_22machine.h"
#include "_22eventList.h"
#ifndef _FACTORYSIM_H_
#define _FACTORYSIM_H_
/*测试函数*/
void factorySimTest();
/*输入工厂数据*/
void inputData();
/*启动仿真*/
void startShop();
/*修改机器状态*/
job* changeState(int theMachine);
/*处理所有任务*/
void simulate();
/*把一项任务移至下一道工序对应的机器*/
bool moveToNextMachine(job* theJob);
/*输出每台机器的等待时间*/
void outputStatistics();
#endif
_22factorySim.cpp
/*
Project name : allAlgorithmsTest
Last modified Date: 2022年8月17日09点22分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 工厂仿真cpp文件,使用了数组队列
*/
#include "_22factorySim.h"
using namespace std;
/*全局变量*/
int timeNow = 0;//当前时间,初始状态为0
int numMachines;//机器数量
int numJobs;//任务数量
eventList* eList;//事件表的指针
machine* mArray;//机器数组
int largeTime = 10000;//在这个时间之前所有机器都已经完成工作
void factorySimTest()
{
inputData();//获取机器和任务的数据
startShop();//装入初始任务
simulate();//执行所有任务
outputStatistics();//输出在每台机器上的等待时间
}
/*输入工厂数据*/
void inputData()
{
//输入工厂数据
cout << "Enter number of machines and jobs:";
while (!(cin >> numMachines>>numJobs))
{
cin.clear();//清空标志位
while (cin.get() != '\n')//删除无效的输入
continue;
cout << "Enter number of machines and jobs:";
}
if (numMachines < 1 || numJobs < 1)
throw illegalInputData("number of machines and jobs must be >=1");
//生成事件和机器队列
eList = new eventList(numMachines, largeTime);//初始化时所有机器都空闲
mArray = new machine[numMachines + 1];//mArray[0]未使用
//输入机器的转换时间
int ct;
for (int j = 1; j <= numMachines; j++)
{
cout << "Enter change-over times for machines " << j << " :";
while (!(cin >> ct))
{
cin.clear();//清空标志位
while (cin.get() != '\n')//删除无效的输入
continue;
cout << "Enter change-over times for machines " << j << " :" ;
}
if (ct < 0)
throw illegalInputData("change-over time must be >= 0");
mArray[j].changeTime = ct;//这里没问题,但是警告我也不知道为什么
}
//输入任务
job* theJob;
int numTasks, firstMachine, theMachine, theTaskTime;
for (int i = 1; i <= numJobs; i++)
{
cout << "Enter number of tasks for job " << i << " :";
while (!(cin >> numTasks))
{
cin.clear();//清空标志位
while (cin.get() != '\n')//删除无效的输入
continue;
cout << "Enter number of tasks for job " << i << " :";
}
firstMachine = 0;//第一道工序的机器
if (numTasks < 1)
throw illegalInputData("each job must have > 1 task");
//生成任务
theJob = new job(i);//job的id为i
cout << "Enter the tasks (machine,time) in process order" << endl;
for (int j = 1; j <= numTasks; j++)
{
while (!(cin >> theMachine>>theTaskTime))
{
cin.clear();//清空标志位
while (cin.get() != '\n')//删除无效的输入
continue;
cout << "Error!Please re-enter:" << endl;
}
if (theMachine < 1 || theTaskTime<1 || theMachine>numMachines)
throw illegalInputData("bad machines number or task time");
if (j == 1)
firstMachine = theMachine;//处理任务的第一台机器
theJob->addTask(theMachine, theTaskTime);
}
mArray[firstMachine].jobQ.push(theJob);//将任务输入到机器的队列中
}
}
/*启动仿真*/
void startShop()
{
//在每台机器上装载其第一个任务
for (int p = 1; p <= numMachines; p++)
changeState(p);
}
/*修改机器状态*/
job* changeState(int theMachine)
{
//机器theMachine上的工序完成了,调度下一道工序
//返回值是在机器theMachine上刚刚完成的任务
job* lastJob;
if (mArray[theMachine].activeJob == nullptr)
{
//处于空闲或转换状态
lastJob = nullptr;
if (mArray[theMachine].jobQ.empty())//没有等待执行的任务
eList->setFinishTime(theMachine, largeTime);
else
{
//从队列中提取任务,在机器上执行
mArray[theMachine].activeJob = mArray[theMachine].jobQ.front();
mArray[theMachine].jobQ.pop();
mArray[theMachine].totalWait += (timeNow - mArray[theMachine].activeJob->arrivalTime);
mArray[theMachine].numTasks++;
cout << "(" << mArray[theMachine].activeJob->taskQ.front().machine << "," << mArray[theMachine].activeJob->taskQ.front().time << ")" << "finished!" << endl;
//cout << "timeNow = " << timeNow << endl;
int t = mArray[theMachine].activeJob->removeNextTask();
eList->setFinishTime(theMachine, timeNow + t);
}
}
else
{
//在机器theMachine上刚刚完成一道工序
//设置转换时间
lastJob = mArray[theMachine].activeJob;
mArray[theMachine].activeJob = nullptr;
eList->setFinishTime(theMachine, timeNow + mArray[theMachine].changeTime);
}
return lastJob;
}
/*处理所有任务*/
void simulate()
{
//处理所有未处理的任务
while (numJobs > 0)
{
//至少有一个任务未处理
int nextToFinish = eList->nextEventMachine();
timeNow = eList->nextEventTime(nextToFinish);
//cout << "sim timeNow = " << timeNow << endl;
//改变机器nextToFinist上的任务
job* theJob = changeState(nextToFinish);
//把任务theJob调度到下一台机器
//如果任务theJob完成,则减少任务数
if (theJob != nullptr && !moveToNextMachine(theJob))
numJobs--;
}
}
/*把一项任务移至下一道工序对应的机器*/
bool moveToNextMachine(job* theJob)
{
//调度任务theJob到执行其下一道工序的机器
//如果任务已经完成,则返回false
if (theJob->taskQ.empty())
{
cout << "Job " << theJob->id << " has completed at " << timeNow <<
" Total wait was " << (timeNow - theJob->length) << endl;
return false;
}
else
{
//任务theJob有下一道工序
//确定执行下一道工序的机器
int p = theJob->taskQ.front().machine;
//把任务插入机器p的等待任务队列
mArray[p].jobQ.push(theJob);
theJob->arrivalTime = timeNow;
//如果机器p空闲,则改变它的状态
if (eList->nextEventTime(p) == largeTime)
changeState(p);
return true;
}
}
/*输出每台机器的等待时间*/
void outputStatistics()
{
cout << "Finish time = " << timeNow << endl;
for (int p = 1; p <= numMachines; p++)
{
cout << "Machine " << p << " completed " << mArray[p].numTasks << " tasks" << endl;
cout << "The total wait time was " << mArray[p].totalWait << endl;
cout << endl;
}
}
_22task.h
每个工序都由两部分构成:machine(执行该工序的机器)和time(完成该工序所需要的时间)。
/*
Project name : allAlgorithmsTest
Last modified Date: 2022年8月17日09点22分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 工序:包括执行该工序的机器machine和完成该工序所需要的时间time
*/
#pragma once
#ifndef _TASK_H_
#define _TASK_H_
#include<iostream>
using std::ostream;
/*工序:包括执行该工序的机器machine和完成该工序所需要的时间time*/
struct task
{
int machine;
int time;
task(int theMachine = 0, int theTime = 0)
{
machine = theMachine;
time = theTime;
}
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const task x)
{
out << "(" << x.machine << "," << x.time << ")";
return out;
}
};
#endif
_22job.h
每项任务都有一个工序表,每道工序按表中的顺序执行。可以把工序表描述成一个队列工taskQ。为了计算一项任务的总等待时间,需要知道该任务的长度和完成时间。完成时间通过计时确定,任务长度为各工序时间之和。为了计算任务长度,我们定义一个数据成员length。
/*
Project name : allAlgorithmsTest
Last modified Date: 2022年8月17日09点22分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 任务
*/
#pragma once
#ifndef _JOB_H_
#define _JOB_H_
#include <queue>
#include "_22task.h"
/*任务*/
struct job
{
queue<task> taskQ;//任务的工序队列
int length;//被调度的工序时间之和
int arrivalTime;//到达当前队列的时间
int id;//任务标识符
job(int theId = 0)
{
id = theId;
length = 0;
arrivalTime = 0;
}
void addTask(int theMachine, int theTime)
{
//添加任务
task theTask(theMachine, theTime);
taskQ.push(theTask);
}
/*删除任务的下一道工序,返回它的时间;更新长度*/
int removeNextTask()
{
int theTime = taskQ.front().time;
taskQ.pop();
length += theTime;
return theTime;
}
};
#endif
_22machine.h
每台机器都有转换时间、当前任务和等待任务的队列。由于每项任务在任何时刻只会在一台机器队列中,因此所有队列的空间总量以任务的数目为限。不过,任务在各个机器队列中的分布随着仿真过程的进展会不断变化。有的队列在某一时刻可能很长。如果使用链队列,就可以把机器队列所需要的空间限制为 n 个节点的空间,其中 n 是任务个数。
/*
Project name : allAlgorithmsTest
Last modified Date: 2022年8月17日09点22分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 机器
*/
#pragma once
#ifndef _MACHINE_H_
#define _MACHINE_H_
#include<queue>
#include "_22job.h"
/*机器*/
struct machine
{
queue<job*> jobQ;//本机器的等待处理的任务队列
int changeTime;//本机器的转换时间
int totalWait;//本机器的总体延时
int numTasks;//本机器处理的工序数量
job* activeJob;//本机器当前处理的任务
machine()
{
changeTime = 0;
totalWait = 0;
numTasks = 0;
activeJob = nullptr;
}
};
#endif
_22eventList.h
所有机器的完成时间都存储在一个事件表中。为了从一个事件转向下一个事件,我们需要在机器的完成时间中确定最小者。仿真器还需要一个操作,来设置一台特定机器的完成时间。每当一个新任务被调度到一台机器上运行时就要执行该操作。当一台机器空闲时,其完成时间被设置成一个很大的数 largeTime。
/*
Project name : allAlgorithmsTest
Last modified Date: 2022年8月17日09点22分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 事件
*/
#pragma once
#ifndef _EVENTLIST_H_
#define _EVENTLIST_H_
class eventList
{
public:
/*为m台机器,初始化其完成时间*/
eventList(int theNumMachines, int theLargeTime)
{
if (theNumMachines < 1)
throw illegalParameterValue("number of machines must be >= 1");
numMachines = theNumMachines;
finishTime = new int[numMachines + 1];
//所有机器都空闲,用大的完成时间初始化
for (int i = 1; i <= numMachines; i++)
finishTime[i] = theLargeTime;
}
/*返回值是处理下一项工序的机器,某个机器完成了*/
int nextEventMachine()
{
int p = 1;
int t = finishTime[1];
for (int i = 2; i <= numMachines; i++)
{
if (finishTime[i] < t)
{
p = i;
t = finishTime[i];
}
}
return p;
}
/*知道处理下一项工序的机器,获取该机器的完成时间*/
int nextEventTime(int theMachine)
{
return finishTime[theMachine];
}
/*设置机器的完成时间*/
void setFinishTime(int theMachine, int theTime)
{
finishTime[theMachine] = theTime;
}
private:
int* finishTime;//机器完成时间数组
int numMachines;//机器数量
};
#endif
_1myExceptions.h
/*
Project name : allAlgorithmsTest
Last modified Date: 2022年8月13日17点38分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 综合各种异常
*/
#pragma once
#ifndef _MYEXCEPTIONS_H_
#define _MYEXCEPTIONS_H_
#include <string>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
// illegal parameter value
class illegalParameterValue
{
public:
illegalParameterValue(string theMessage = "Illegal parameter value")
{
message = theMessage;}
void outputMessage() {
cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
// illegal input data
class illegalInputData
{
public:
illegalInputData(string theMessage = "Illegal data input")
{
message = theMessage;}
void outputMessage() {
cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
// illegal index
class illegalIndex
{
public:
illegalIndex(string theMessage = "Illegal index")
{
message = theMessage;}
void outputMessage() {
cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
// matrix index out of bounds
class matrixIndexOutOfBounds
{
public:
matrixIndexOutOfBounds
(string theMessage = "Matrix index out of bounds")
{
message = theMessage;}
void outputMessage() {
cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
// matrix size mismatch
class matrixSizeMismatch
{
public:
matrixSizeMismatch(string theMessage =
"The size of the two matrics doesn't match")
{
message = theMessage;}
void outputMessage() {
cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
// stack is empty
class stackEmpty
{
public:
stackEmpty(string theMessage =
"Invalid operation on empty stack")
{
message = theMessage;}
void outputMessage() {
cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
// queue is empty
class queueEmpty
{
public:
queueEmpty(string theMessage =
"Invalid operation on empty queue")
{
message = theMessage;}
void outputMessage() {
cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
// hash table is full
class hashTableFull
{
public:
hashTableFull(string theMessage =
"The hash table is full")
{
message = theMessage;}
void outputMessage() {
cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
// edge weight undefined
class undefinedEdgeWeight
{
public:
undefinedEdgeWeight(string theMessage =
"No edge weights defined")
{
message = theMessage;}
void outputMessage() {
cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
// method undefined
class undefinedMethod
{
public:
undefinedMethod(string theMessage =
"This method is undefined")
{
message = theMessage;}
void outputMessage() {
cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
#endif
运行结果
"C:\Users\15495\Documents\Jasmine\prj\_Algorithm\Data Structures, Algorithms and Applications in C++\_19Factory simulation\cmake-build-debug\_19Factory_simulation.exe"
Enter number of machines and jobs:3 4
Enter change-over times for machines 1 :2
Enter change-over times for machines 2 :3
Enter change-over times for machines 3 :1
Enter number of tasks for job 1 :3
Enter the tasks (machine,time) in process order
1 2
2 4
1 1
Enter number of tasks for job 2 :2
Enter the tasks (machine,time) in process order
3 4
1 2
Enter number of tasks for job 3 :2
Enter the tasks (machine,time) in process order
1 4
2 4
Enter number of tasks for job 4 :2
Enter the tasks (machine,time) in process order
3 1
2 3
(1,2)finished!
(3,4)finished!
(2,4)finished!
(1,4)finished!
(3,1)finished!
(2,3)finished!
(1,2)finished!
Job 2 has completed at 12 Total wait was 6
Job 4 has completed at 12 Total wait was 8
(1,1)finished!
Job 1 has completed at 15 Total wait was 8
(2,4)finished!
Job 3 has completed at 19 Total wait was 11
Finish time = 19
Machine 1 completed 4 tasks
The total wait time was 18
Machine 2 completed 3 tasks
The total wait time was 10
Machine 3 completed 2 tasks
The total wait time was 5
Process finished with exit code 0
更多【算法-《数据结构、算法与应用C++语言描述》-队列的应用-工厂仿真】相关视频教程:www.yxfzedu.com
相关文章推荐
- log4j-项目实战:中央控制器实现(2)-优化Controller,将共性动作抽取到中央控制器 - 其他
- 聚类-数据挖掘:分类,聚类,关联关系,回归 - 其他
- objective-c-http客户端简单demo - 其他
- 编程技术-自然语言处理实战项目21-两段文本的查重功能,返回最相似的文本字符串,可应用于文本查重与论文查重 - 其他
- 编程技术-基于教与学算法优化概率神经网络PNN的分类预测 - 附代码 - 其他
- 运维-linux生产者消费者模型 - 其他
- 编程技术-微服务概览 - 其他
- 算法-基于python+TensorFlow+Django卷积网络算法+深度学习模型+蔬菜识别系统 - 其他
- 计算机外设-【PyQt】(自制类)处理鼠标点击逻辑 - 其他
- css-Module build failed (from ./node_modules/postcss-loader/src/index.js): - 其他
- java-【TiDB】TiDB CLuster部署 - 其他
- tidb-KCC@广州与 TiDB 社区联手—广州开源盛宴 - 其他
- pdf-耗时3年写了一本数据结构与算法pdf!开源了 - 其他
- 计算机外设-键盘win键无法使用,win+r不生效、win键没反应、Windows键失灵解决方案(亲测可以解决) - 其他
- 计算机外设-键盘打字盲打练习系列之认识键盘——0 - 其他
- 机器学习-Azure 机器学习 - 有关为 Azure 机器学习配置 Kubernetes 群集的参考 - 其他
- 信息可视化-ESP32网络开发实例-将数据保存到InfluxDB时序数据库 - 其他
- 计算机外设-基于QT使用OpenGL,加载obj模型,进行鼠标交互 - 其他
- 前端框架-React进阶之路(三)-- Hooks - 其他
- 运维-python实现炒股自动化,个人账户无门槛量化交易的开始 - 其他
2):严禁色情、血腥、暴力
3):严禁发布任何形式的广告贴
4):严禁发表关于中国的政治类话题
5):严格遵守中国互联网法律法规
6):有侵权,疑问可发邮件至service@yxfzedu.com
- ar-Angular 由一个bug说起之一:List / Grid的性能问题
- vr-VR全景技术,为养老院宣传推广带来全新变革
- 网络-【广州华锐互动】VR安防网络综合布线仿真实训打造沉浸式的教学体验
- list-使用多线程处理List数据
- vr-【广州华锐互动】楼宇智能化VR虚拟教学系统
- 笔记-FreeRTOS源码阅读笔记2--list.c
- react.js-Antd React Form.Item内部是自定义组件怎么自定义返回值
- 区块链-2023年A股借壳上市研究报告
- spring-Spring Boot中处理简单的事务
- 网络-【hcie-cloud】【4】华为云Stack规划设计之华为云Stack标准组网【中】