Android安全-Key Attestation原理理解
推荐 原创【Android安全-Key Attestation原理理解】此文章归类为:Android安全。
结合github项目KeyAttestation来学习KeyAttestation原理
一、项目结构
1.1 App展示
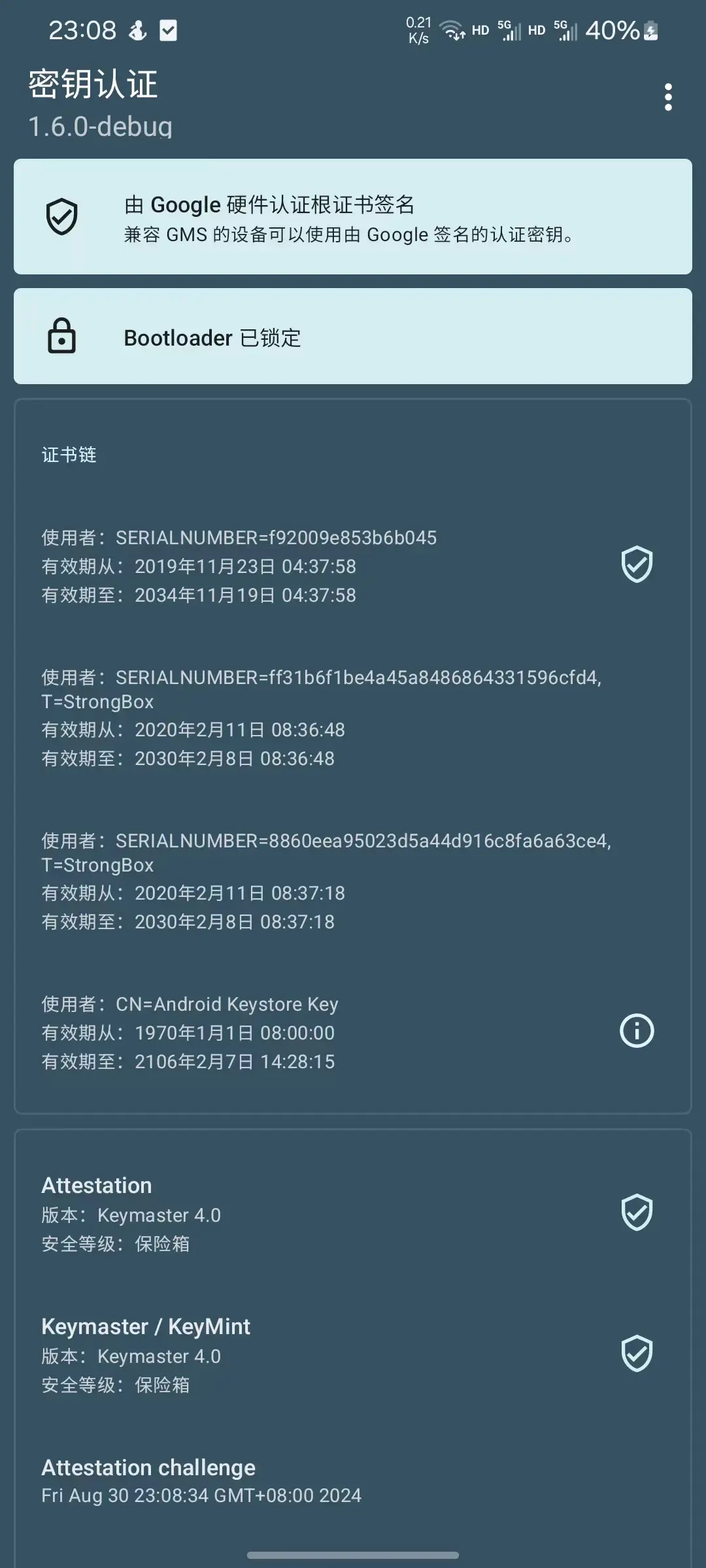

页面展示来自于attestationResult这个回调结果
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 | // app/src/main/java/io/github/vvb2060/keyattestation/home/HomeViewModel.ktval useStrongBox = hasStrongBox && preferStrongBoxval includeProps = hasDeviceIds && preferIncludePropsval useAttestKey = hasAttestKey && preferAttestKeyval result = try { val attestationResult = doAttestation(useStrongBox, includeProps, useAttestKey) Resource.success(attestationResult)} catch (e: Throwable) { val cause = if (e is AttestationException) e.cause else e Log.w(AppApplication.TAG, "Do attestation error.", cause) when (e) { is AttestationException -> Resource.error(e, null) else -> Resource.error(AttestationException(CODE_UNKNOWN, e), null) }} |
1.2 初步梳理流程
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 | // app/src/main/java/io/github/vvb2060/keyattestation/home/HomeViewModel.kt@Throws(AttestationException::class)private fun doAttestation(useStrongBox: Boolean, includeProps: Boolean, useAttestKey: Boolean): AttestationResult { val certs = ArrayList<Certificate>() val alias = if (useStrongBox) "${AppApplication.TAG}_strongbox" else AppApplication.TAG val attestKeyAlias = if (useAttestKey) "${alias}_persistent" else null try { // 1. generateKey if (useAttestKey && !keyStore.containsAlias(attestKeyAlias)) { generateKey(attestKeyAlias!!, useStrongBox, includeProps, attestKeyAlias) } generateKey(alias, useStrongBox, includeProps, attestKeyAlias) // 2. certs collect val certChain = keyStore.getCertificateChain(alias) ?: throw CertificateException("Unable to get certificate chain") for (cert in certChain) { val buf = ByteArrayInputStream(cert.encoded) certs.add(certificateFactory.generateCertificate(buf)) } if (useAttestKey) { val persistChain = keyStore.getCertificateChain(attestKeyAlias) ?: throw CertificateException("Unable to get certificate chain") for (cert in persistChain) { val buf = ByteArrayInputStream(cert.encoded) certs.add(certificateFactory.generateCertificate(buf)) } } } catch (e: ProviderException) { // 异常流程,可忽略 ...... } catch (e: Exception) { throw AttestationException(CODE_UNKNOWN, e) } @Suppress("UNCHECKED_CAST") // 3. parseCertificateChain currentCerts = certs as List<X509Certificate> return parseCertificateChain(certs)} |
从代码流程中可以分为三步
- generateKey
- certs collect
- parseCertificateChain
二、源码分析
2.1 入参
doAttestation的入参有三个
- useStrongBox
- includeProps
- useAttestKey
获取方式是
1 2 3 4 5 | // android.hardware.strongbox_keystoreuseStrongBox = pm.hasSystemFeature(PackageManager.FEATURE_STRONGBOX_KEYSTORE)// android.hardware.keystore.app_attest_keyhasAttestKey = pm.hasSystemFeature(PackageManager.FEATURE_KEYSTORE_APP_ATTEST_KEY)hasDeviceIds = pm.hasSystemFeature("android.software.device_id_attestation") |
是从PackageManager中获取系统属性,这三个属性指的是什么意思呢?这里需要引入Android KeyStore的演变历史
KeyStore是借助系统芯片 (SoC) 中提供的可信执行环境,由硬件支持的密钥库
- KeyMaster 0.2 0.3
在 Android 6.0 之前的版本中,Android 已有一个非常简单的由硬件支持的加密服务 API(由 0.2 和 0.3 版的 Keymaster 硬件抽象层 (HAL) 提供)。该密钥库能够提供数字签名和验证操作,以及不对称签名密钥对的生成和导入操作。该 API 在许多设备上都已实现,但有许多安全目标无法只通过一个签名 API 来轻松达成。Android 6.0 中的密钥库在该密钥库 API 的基础上进行了扩展,能够提供更广泛的功能
- KeyMaster 1
在 Android 6.0 中,密钥库不仅增加了对称加密基元(AES 和 HMAC),还增加了针对由硬件支持的密钥的访问权限控制系统。访问权限控制在密钥生成期间指定,并会在密钥的整个生命周期内被强制执行。可以将密钥限定为仅在用户通过身份验证后才可使用,并且只能用于指定的目的或只有在具有指定的加密参数时才可使用。如需了解详情,请参阅授权标记和函数页面。
- KeyMaster 2
在 Android 7.0 中,Keymaster 2 增加了对密钥认证和版本绑定的支持。密钥认证提供公钥证书,这些证书中包含密钥及其访问权限控制的详细描述,以使密钥存在于安全硬件中并使其配置可以远程验证。
- KeyMaster 3
在 Android 8.0 中,Keymaster 3 从旧式 C 结构硬件抽象层 (HAL) 转换到根据新硬件接口定义语言 (HIDL) 中的定义生成的 C++ HAL 接口。在此变更过程中,很多参数类型发生了变化,但这些类型和方法与旧的类型和 HAL 结构体方法一一对应。如需了解详情,请参阅函数页面
除了此接口修订之外,Android 8.0 还扩展了 Keymaster 2 的认证功能,以支持 ID 认证。 ID 认证提供了一种受限且可选的机制来严格认证硬件标识符,例如设备序列号、产品名称和手机 ID (IMEI/MEID)。为了实现此新增功能,Android 8.0 更改了 ASN.1 认证架构,添加了 ID 认证。Keymaster 实现需要通过某种安全方式来检索相关的数据项,还需要定义一种安全永久地停用该功能的机制。
- KeyMaster 4
Android 9 纳入了以下更新:
更新到 Keymaster 4
对嵌入式安全元件的支持
对安全密钥导入的支持
对 3DES 加密的支持
更改了版本绑定,以便 boot.img 和 system.img 分别设置版本以允许独立更新
从KeyStore的版本演变上看,在迭代过程中逐步加入了新的认证方式,而FEATURE_STRONGBOX_KEYSTORE、FEATURE_KEYSTORE_APP_ATTEST_KEY就是判断设备是否支持某种认证方式(原因是因为OEM厂商不一定会紧跟着Google的架构演变方案)
2.2 generateKey
1 2 3 4 | if (useAttestKey && !keyStore.containsAlias(attestKeyAlias)) { generateKey(attestKeyAlias!!, useStrongBox, includeProps, attestKeyAlias)}generateKey(alias, useStrongBox, includeProps, attestKeyAlias) |
这里区分了生成key的类型,如果设备开启了App Attest Key特性的话生成的密钥可以用来做密钥认证(Key Attestation),否则就是正常的数字签名密钥
这里优先根据是否开启了App Attest Key特性及KeyStore中是否包含attestKeyAlias的密钥来进行密钥生成
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 | private fun generateKey(alias: String, useStrongBox: Boolean, includeProps: Boolean, attestKeyAlias: String?) { val now = Date() val attestKey = alias == attestKeyAlias // 密钥用途判定 val purposes = if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.S && attestKey) { KeyProperties.PURPOSE_ATTEST_KEY } else { KeyProperties.PURPOSE_SIGN } // 设置 KeyGenParameterSpec val builder = KeyGenParameterSpec.Builder(alias, purposes) .setAlgorithmParameterSpec(ECGenParameterSpec("secp256r1")) .setDigests(KeyProperties.DIGEST_SHA256) .setCertificateNotBefore(now) .setAttestationChallenge(now.toString().toByteArray()) if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.P && useStrongBox) { builder.setIsStrongBoxBacked(true) } if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.S) { if (includeProps) { builder.setDevicePropertiesAttestationIncluded(true) } if (attestKey) { builder.setCertificateSubject(X500Principal("CN=App Attest Key")) } else { builder.setAttestKeyAlias(attestKeyAlias) } } // 获取 KeyPairGenerator 实例 val keyPairGenerator = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance( KeyProperties.KEY_ALGORITHM_EC, "AndroidKeyStore") // 用 KeyGenParameterSpec 初始化 KeyPairGenerator keyPairGenerator.initialize(builder.build()) // 生成密钥对 keyPairGenerator.generateKeyPair()} |
此时,KeyStore中包含了名称为alias的密钥对
2.3 certs collect
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | val certChain = keyStore.getCertificateChain(alias) ?: throw CertificateException("Unable to get certificate chain")for (cert in certChain) { val buf = ByteArrayInputStream(cert.encoded) certs.add(certificateFactory.generateCertificate(buf))}if (useAttestKey) { val persistChain = keyStore.getCertificateChain(attestKeyAlias) ?: throw CertificateException("Unable to get certificate chain") for (cert in persistChain) { val buf = ByteArrayInputStream(cert.encoded) certs.add(certificateFactory.generateCertificate(buf)) }} |
在上一步生成key之后根据alias获取到对应的证书链,证书链是一个认证过程,最终指向可信的根证书,因此获取到的证书链实际的形式是
终端证书->中间证书->根证书
2.4 parseCertificateChain
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 | // app/src/main/java/io/github/vvb2060/keyattestation/attestation/CertificateInfo.javapublic static AttestationResult parseCertificateChain(List<X509Certificate> certs) { var infoList = new ArrayList<CertificateInfo>(); // 在certs中最后一个指向的是终端证书,逐步向上遍历 var parent = certs.get(certs.size() - 1); for (int i = certs.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) { var parentKey = parent.getPublicKey(); var info = new CertificateInfo(certs.get(i)); infoList.add(info); info.checkStatus(parentKey); if (parent == info.cert) { info.checkIssuer(); } else { parent = info.cert; } if (info.checkAttestation()) { break; } }return AttestationResult.form(infoList); |
遍历证书列表,进行三次校验
- checkStatus
- checkIssuer
- checkAttestation
2.4.1 checkStatus
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | // app/src/main/java/io/github/vvb2060/keyattestation/attestation/CertificateInfo.javaprivate void checkStatus(PublicKey parentKey) { try { status = CERT_SIGN; cert.verify(parentKey); status = CERT_REVOKED; var certStatus = RevocationList.get(cert.getSerialNumber()); if (certStatus != null) { throw new CertificateException("Certificate revocation " + certStatus); } status = CERT_EXPIRED; cert.checkValidity(); status = CERT_NORMAL; } catch (GeneralSecurityException e) { securityException = e; }} |
在checkStatus函数中存在状态流转的过程,涉及到两个函数verify、checkValidity,主要目的是为了确保一个证书的签名是有效的、且被信任的上级证书所签发
2.4.2 checkIssuer
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 | // app/src/main/java/io/github/vvb2060/keyattestation/attestation/CertificateInfo.javaprivate void checkIssuer() { var publicKey = cert.getPublicKey().getEncoded(); if (Arrays.equals(publicKey, googleKey)) { issuer = KEY_GOOGLE; } else if (Arrays.equals(publicKey, aospEcKey)) { issuer = KEY_AOSP; } else if (Arrays.equals(publicKey, aospRsaKey)) { issuer = KEY_AOSP; } else if (Arrays.equals(publicKey, knoxSakv2Key)) { issuer = KEY_KNOX; } else if (oemKeys != null) { for (var key : oemKeys) { if (Arrays.equals(publicKey, key.getEncoded())) { issuer = KEY_OEM; break; } } }} |
这一步是为了确定根证书的颁发机构,其中获取OEM Key的方式如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 | private static Set<PublicKey> getOemPublicKey() { var resName = "android:array/vendor_required_attestation_certificates"; var res = AppApplication.app.getResources(); // noinspection DiscouragedApi var id = res.getIdentifier(resName, null, null); if (id == 0) { return null; } var set = new HashSet<PublicKey>(); try { var cf = CertificateFactory.getInstance("X.509"); for (var s : res.getStringArray(id)) { var cert = s.replaceAll("\\s+", "\n") .replaceAll("-BEGIN\\nCERTIFICATE-", "-BEGIN CERTIFICATE-") .replaceAll("-END\\nCERTIFICATE-", "-END CERTIFICATE-"); var input = new ByteArrayInputStream(cert.getBytes()); var publicKey = cf.generateCertificate(input).getPublicKey(); set.add(publicKey); } } catch (CertificateException e) { Log.e(AppApplication.TAG, "getOemKeys: ", e); return null; } set.removeIf(key -> Arrays.equals(key.getEncoded(), googleKey)); if (set.isEmpty()) { return null; } set.forEach(key -> Log.i(AppApplication.TAG, "getOemKeys: " + key)); return set;} |
2.4.3 checkAttestation
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 | // app/src/main/java/io/github/vvb2060/keyattestation/attestation/CertificateInfo.javaprivate boolean checkAttestation() { boolean terminate; try { attestation = Attestation.loadFromCertificate(cert); // If key purpose included KeyPurpose::SIGN, // then it could be used to sign arbitrary data, including any tbsCertificate, // and so an attestation produced by the key would have no security properties. // If the parent certificate can attest that the key purpose is only KeyPurpose::ATTEST_KEY, // then the child certificate can be trusted. var purposes = attestation.getTeeEnforced().getPurposes(); terminate = purposes == null || !purposes.contains(AuthorizationList.KM_PURPOSE_ATTEST_KEY); } catch (CertificateParsingException e) { certException = e; terminate = false; checkProvisioningInfo(); } return terminate;}// app/src/main/java/io/github/vvb2060/keyattestation/attestation/Attestation.javapublic static Attestation loadFromCertificate(X509Certificate x509Cert) throws CertificateParsingException { if (x509Cert.getExtensionValue(EAT_OID) == null && x509Cert.getExtensionValue(ASN1_OID) == null) { throw new CertificateParsingException("No attestation extensions found"); } if (x509Cert.getExtensionValue(EAT_OID) != null) { if (x509Cert.getExtensionValue(ASN1_OID) != null) { throw new CertificateParsingException("Multiple attestation extensions found"); } try { return new EatAttestation(x509Cert); } catch (CborException cbe) { throw new CertificateParsingException("Unable to parse EAT extension", cbe); } } if (x509Cert.getExtensionValue(CRL_DP_OID) != null) { Log.w(AppApplication.TAG, "CRL Distribution Points extension found in leaf certificate."); } if (x509Cert.getExtensionValue(KNOX_OID) != null) { return new KnoxAttestation(x509Cert); } return new Asn1Attestation(x509Cert);} |
根据代码逻辑的理解,是根据证书颁发机构来选择各自的认证方式
2.4.3.1 EatAttestation
EatAttestation使用实体认证令牌 (Entity Attestation Token, EAT) 进行设备认证。EAT是一种基于IETF标准的轻量级认证格式,场景更多的是存在嵌入到IoT设备中
2.4.3.2 KnoxAttestation
三星电子提供的一种设备认证和安全机制,核心逻辑还是走的Asn1
2.4.3.3 Asn1Attestation
重点关注下Asn1的认证方式,也是官方选择的认证方式,参考文档security-key-attestation
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 | // app/src/main/java/io/github/vvb2060/keyattestation/attestation/Asn1Attestation.javapublic Asn1Attestation(X509Certificate x509Cert) throws CertificateParsingException { super(x509Cert); ASN1Sequence seq = getAttestationSequence(x509Cert); attestationVersion = Asn1Utils.getIntegerFromAsn1(seq.getObjectAt(ATTESTATION_VERSION_INDEX)); attestationSecurityLevel = Asn1Utils.getIntegerFromAsn1(seq.getObjectAt(ATTESTATION_SECURITY_LEVEL_INDEX)); keymasterVersion = Asn1Utils.getIntegerFromAsn1(seq.getObjectAt(KEYMASTER_VERSION_INDEX)); keymasterSecurityLevel = Asn1Utils.getIntegerFromAsn1(seq.getObjectAt(KEYMASTER_SECURITY_LEVEL_INDEX)); attestationChallenge = Asn1Utils.getByteArrayFromAsn1(seq.getObjectAt(ATTESTATION_CHALLENGE_INDEX)); uniqueId = Asn1Utils.getByteArrayFromAsn1(seq.getObjectAt(UNIQUE_ID_INDEX)); softwareEnforced = new AuthorizationList(seq.getObjectAt(SW_ENFORCED_INDEX)); teeEnforced = new AuthorizationList(seq.getObjectAt(TEE_ENFORCED_INDEX));} |
根据传入的x509Cert解析成各个字段,这里可以参考ASN.1架构
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 | KeyDescription ::= SEQUENCE { attestationVersion INTEGER, # KM2 value is 1. KM3 value is 2. KM4 value is 3. attestationSecurityLevel SecurityLevel, keymasterVersion INTEGER, keymasterSecurityLevel SecurityLevel, attestationChallenge OCTET_STRING, uniqueId OCTET_STRING, softwareEnforced AuthorizationList, teeEnforced AuthorizationList,}SecurityLevel ::= ENUMERATED { Software (0), TrustedEnvironment (1), StrongBox (2),}AuthorizationList ::= SEQUENCE { purpose [1] EXPLICIT SET OF INTEGER OPTIONAL, algorithm [2] EXPLICIT INTEGER OPTIONAL, keySize [3] EXPLICIT INTEGER OPTIONAL. digest [5] EXPLICIT SET OF INTEGER OPTIONAL, padding [6] EXPLICIT SET OF INTEGER OPTIONAL, ecCurve [10] EXPLICIT INTEGER OPTIONAL, rsaPublicExponent [200] EXPLICIT INTEGER OPTIONAL, rollbackResistance [303] EXPLICIT NULL OPTIONAL, # KM4 activeDateTime [400] EXPLICIT INTEGER OPTIONAL originationExpireDateTime [401] EXPLICIT INTEGER OPTIONAL usageExpireDateTime [402] EXPLICIT INTEGER OPTIONAL noAuthRequired [503] EXPLICIT NULL OPTIONAL, userAuthType [504] EXPLICIT INTEGER OPTIONAL, authTimeout [505] EXPLICIT INTEGER OPTIONAL, allowWhileOnBody [506] EXPLICIT NULL OPTIONAL, trustedUserPresenceRequired [507] EXPLICIT NULL OPTIONAL, # KM4 trustedConfirmationRequired [508] EXPLICIT NULL OPTIONAL, # KM4 unlockedDeviceRequired [509] EXPLICIT NULL OPTIONAL, # KM4 allApplications [600] EXPLICIT NULL OPTIONAL, applicationId [601] EXPLICIT OCTET_STRING OPTIONAL, creationDateTime [701] EXPLICIT INTEGER OPTIONAL, origin [702] EXPLICIT INTEGER OPTIONAL, rollbackResistant [703] EXPLICIT NULL OPTIONAL, # KM2 and KM3 only. rootOfTrust [704] EXPLICIT RootOfTrust OPTIONAL, osVersion [705] EXPLICIT INTEGER OPTIONAL, osPatchLevel [706] EXPLICIT INTEGER OPTIONAL, attestationApplicationId [709] EXPLICIT OCTET_STRING OPTIONAL, # KM3 attestationIdBrand [710] EXPLICIT OCTET_STRING OPTIONAL, # KM3 attestationIdDevice [711] EXPLICIT OCTET_STRING OPTIONAL, # KM3 attestationIdProduct [712] EXPLICIT OCTET_STRING OPTIONAL, # KM3 attestationIdSerial [713] EXPLICIT OCTET_STRING OPTIONAL, # KM3 attestationIdImei [714] EXPLICIT OCTET_STRING OPTIONAL, # KM3 attestationIdMeid [715] EXPLICIT OCTET_STRING OPTIONAL, # KM3 attestationIdManufacturer [716] EXPLICIT OCTET_STRING OPTIONAL, # KM3 attestationIdModel [717] EXPLICIT OCTET_STRING OPTIONAL, # KM3 vendorPatchLevel [718] EXPLICIT INTEGER OPTIONAL, # KM4 bootPatchLevel [719] EXPLICIT INTEGER OPTIONAL, # KM4}RootOfTrust ::= SEQUENCE { verifiedBootKey OCTET_STRING, deviceLocked BOOLEAN, verifiedBootState VerifiedBootState, verifiedBootHash OCTET_STRING, # KM4}VerifiedBootState ::= ENUMERATED { Verified (0), SelfSigned (1), Unverified (2), Failed (3),} |
checkAttestation的核心是
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 | // app/src/main/java/io/github/vvb2060/keyattestation/attestation/CertificateInfo.java// If key purpose included KeyPurpose::SIGN,// then it could be used to sign arbitrary data, including any tbsCertificate,// and so an attestation produced by the key would have no security properties.// If the parent certificate can attest that the key purpose is only KeyPurpose::ATTEST_KEY,// then the child certificate can be trusted.var purposes = attestation.getTeeEnforced().getPurposes();terminate = purposes == null || !purposes.contains(AuthorizationList.KM_PURPOSE_ATTEST_KEY);// app/src/main/java/io/github/vvb2060/keyattestation/attestation/AuthorizationList.javapublic AuthorizationList(ASN1Encodable asn1Encodable) throws CertificateParsingException { if (!(asn1Encodable instanceof ASN1Sequence sequence)) { throw new CertificateParsingException("Expected sequence for authorization list, found " + asn1Encodable.getClass().getName()); } for (var entry : sequence) { if (!(entry instanceof ASN1TaggedObject taggedObject)) { throw new CertificateParsingException( "Expected tagged object, found " + entry.getClass().getName()); } int tag = taggedObject.getTagNo(); var value = taggedObject.getBaseObject().toASN1Primitive(); switch (tag) { default: throw new CertificateParsingException("Unknown tag " + tag + " found"); case KM_TAG_PURPOSE & KEYMASTER_TAG_TYPE_MASK: purposes = Asn1Utils.getIntegersFromAsn1Set(value); break; } }} |
核心是要证明teeEnforced的purpose字段,根据上面那段注释我理解是将密钥用途分为了签名和认证
- 签名用途 (KeyPurpose::SIGN):
如果密钥的用途包含签名,那么它可以对任意数据进行签名。这种情况下,持有该密钥的实体可以签名任何数据,包括认证证书自身 (tbsCertificate)。若如此,这个密钥生成的认证就没有任何实际的安全保证,因为任何人都可以在任意数据上应用该签名,伪装成合法的认证。签名的真实性无法被保障 - 认证用途 (KeyPurpose::ATTEST_KEY):
如果密钥用途被正确设定为仅用于认证 (KeyPurpose::ATTEST_KEY),那么该密钥只能用于生成认证证书,而不能用于签名任意数据。在这种情况下,父证书可以证明子证书的密钥用途仅限于认证,从而确保子证书的可信度。这种可信度依赖于父证书的有效性,也就是根证书的可信度
这里引入了认证的源头:根证书的可信度问题
Andorid通过Trusty TEE完成证书的存储,TEE在硬件层面解决了安全性问题,其中类似RootOfTrust这类数据都是由厂商在设备出产时烧录到硬件存储当中的,从根本上解决了根密钥不可信的问题,并以此根密钥为信任链根,派生密钥
三. 总结
可以利用KeyAttestation来做什么呢?
- 验证密钥可信性
密钥认证用于验证设备上的密钥是否由可信的安全硬件生成。通过密钥认证,App可以确保密钥没有被复制或篡改,并且确实是在受信任的环境中创建的 - 设备身份和完整性验证
密钥认证可以用于验证设备的身份和完整性。通过认证过程中提供的证明数据(比如设备标识符、硬件特性等),可以保证设备没有被篡改或替换
更多【Android安全-Key Attestation原理理解】相关视频教程:www.yxfzedu.com
相关文章推荐
- 企业安全-学习Kubernetes笔记——部署web站点环境(PHP+Nginx) - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 企业安全-学习Kubernetes笔记——安装NFS驱动 - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 企业安全-学习Kubernetes笔记——kubeadm安装Kubernetes - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 软件逆向-wibu软授权(四) - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 软件逆向-使用IDAPython开发复制RVA的插件 - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 2-wibu软授权(三) - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 软件逆向-wibu软授权(二) - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 软件逆向-wibu软授权(一) - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 软件逆向- PE格式:分析IatHook并实现 - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- Android安全-安卓API自动化安全扫描 - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 二进制漏洞- Chrome v8 Issue 1307610漏洞及其利用分析 - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- iOS安全-IOS 脱壳入坑经验分享 - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 二进制漏洞-Windows UAF 漏洞分析CVE-2014-4113 - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- CTF对抗-lua 逆向学习 & RCTF picstore 还原代码块 - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- Android安全-如何修改unity HybridCLR 热更dll - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 软件逆向-浅谈编译器对代码的优化 - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 二进制漏洞-年终CLFS漏洞汇总分析 - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 软件逆向-自动化提取恶意文档中的shellcode - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 二进制漏洞-铁威马TerraMaster CVE-2022-24990&CVE-2022-24989漏洞分析报告 - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
- 4-seccomp-bpf+ptrace实现修改系统调用原理(附demo) - Android安全CTF对抗IOS安全
2):严禁色情、血腥、暴力
3):严禁发布任何形式的广告贴
4):严禁发表关于中国的政治类话题
5):严格遵守中国互联网法律法规
6):有侵权,疑问可发邮件至service@yxfzedu.com