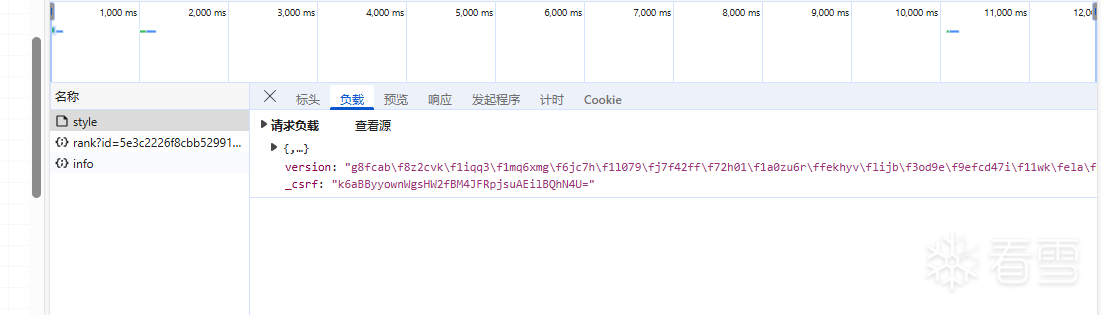
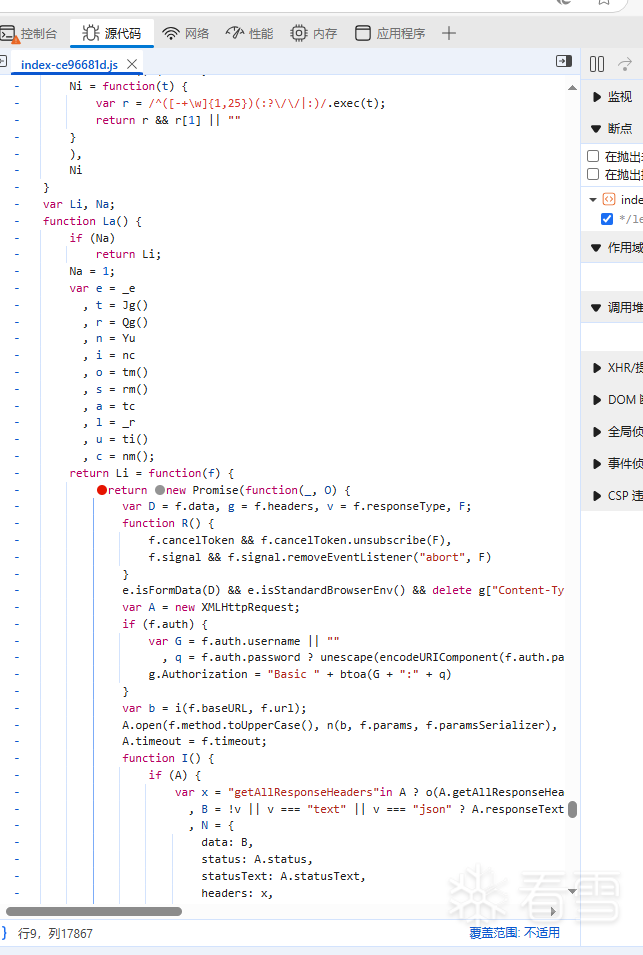
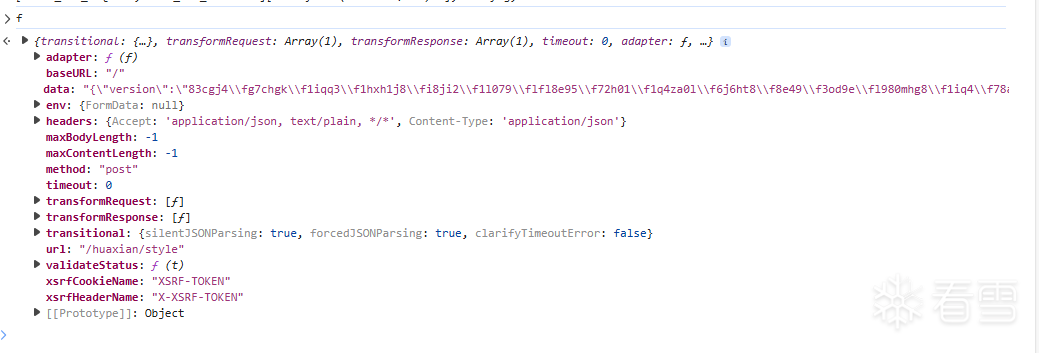
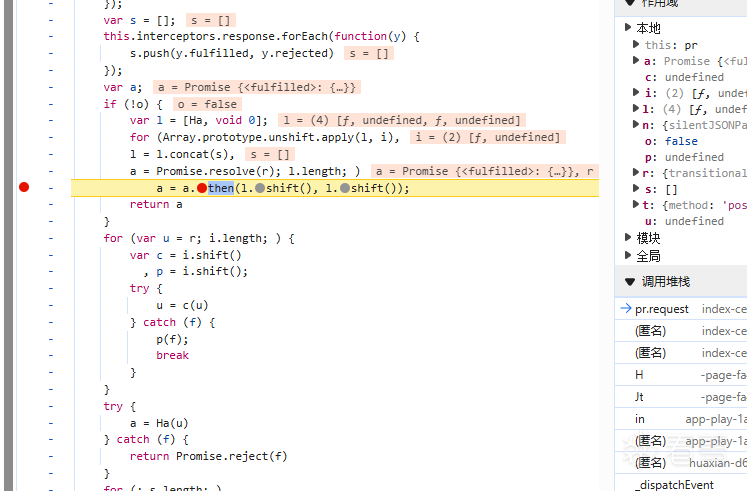
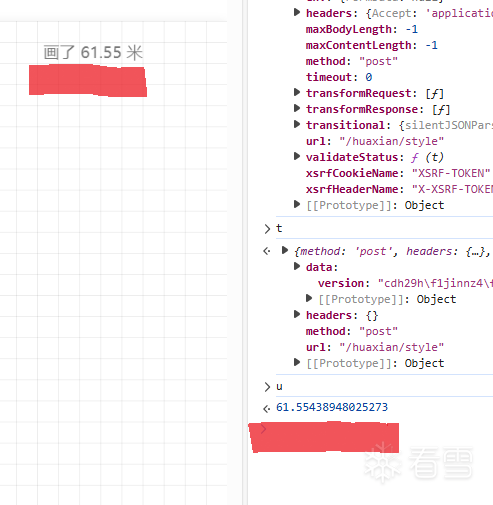
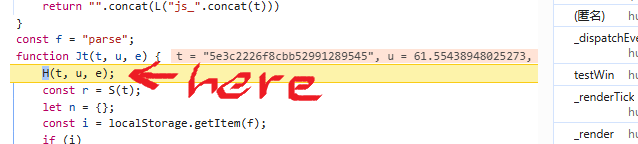
WEB安全-逆向一小游戏的成绩提交代码
推荐 原创更多【WEB安全-逆向一小游戏的成绩提交代码】相关视频教程:www.yxfzedu.com
相关文章推荐
- 二进制漏洞-零基础入门V8——CVE-2021-38001漏洞利用 - PwnHarmonyOSWeb安全软件逆向
- 二进制漏洞-初探内核漏洞:HEVD学习笔记——UAF - PwnHarmonyOSWeb安全软件逆向
- Pwn-glibc高版本堆题攻击之safe unlink - PwnHarmonyOSWeb安全软件逆向
- 二进制漏洞-CVE-2020-1054提权漏洞学习笔记 - PwnHarmonyOSWeb安全软件逆向
- 二进制漏洞-初探内核漏洞:HEVD学习笔记——BufferOverflowNonPagedPool - PwnHarmonyOSWeb安全软件逆向
- CTF对抗-2022DASCTF Apr X FATE 防疫挑战赛-Reverse-奇怪的交易 - PwnHarmonyOSWeb安全软件逆向
- 编程技术-一个规避安装包在当前目录下被DLL劫持的想法 - PwnHarmonyOSWeb安全软件逆向
- CTF对抗-sql注入学习笔记 - PwnHarmonyOSWeb安全软件逆向
- Pwn-DamCTF and Midnight Sun CTF Qualifiers pwn部分wp - PwnHarmonyOSWeb安全软件逆向
- 软件逆向-OLLVM-deflat 脚本学习 - PwnHarmonyOSWeb安全软件逆向
- 软件逆向-3CX供应链攻击样本分析 - PwnHarmonyOSWeb安全软件逆向
- Android安全-某艺TV版 apk 破解去广告及源码分析 - PwnHarmonyOSWeb安全软件逆向
- Pwn-Hack-A-Sat 4 Qualifiers pwn部分wp - PwnHarmonyOSWeb安全软件逆向
- 二进制漏洞- AFL 源代码速通笔记 - PwnHarmonyOSWeb安全软件逆向
- 二进制漏洞-Netatalk CVE-2018-1160 复现及漏洞利用思路 - PwnHarmonyOSWeb安全软件逆向
- 二进制漏洞-DynamoRIO源码分析(一)--劫持进程 - PwnHarmonyOSWeb安全软件逆向
- 二进制漏洞-通用shellcode开发原理与实践 - PwnHarmonyOSWeb安全软件逆向
- Android安全-frida-server运行报错问题的解决 - PwnHarmonyOSWeb安全软件逆向
- Android安全-记一次中联X科的试岗实战项目 - PwnHarmonyOSWeb安全软件逆向
- Android安全-对SM-P200平板的root记录 - PwnHarmonyOSWeb安全软件逆向
记录自己的技术轨迹
文章规则:
1):文章标题请尽量与文章内容相符
2):严禁色情、血腥、暴力
3):严禁发布任何形式的广告贴
4):严禁发表关于中国的政治类话题
5):严格遵守中国互联网法律法规
6):有侵权,疑问可发邮件至service@yxfzedu.com
近期原创 更多